Top Scrum Master Interview Questions in 2025 (With Tips)

The role of a Scrum Master has grown significantly in recent years. It’s no longer just about running stand-ups or facilitating retrospectives. In 2025, organizations expect Scrum Masters to guide teams, influence leadership, drive agile transformation, and sometimes even understand AI-driven workflows. If you’re preparing for a Scrum Master interview, it’s essential to go beyond textbook answers. Here are the top Scrum Master interview questions being asked in 2025 — and what interviewers are really looking for. 🔹 1. How do you handle resistance to Agile from senior leadership? Why they ask: Companies still struggle with top-down resistance to Agile. Interviewers want to know if you can communicate value to leadership without creating conflict. Pro Tip: Share real-life examples, and talk about how you used metrics, workshops, or pilot teams to earn buy-in. 🔹 2. What metrics do you use to measure team performance in Scrum? Why they ask: Velocity alone is no longer enough. Modern teams focus on value, predictability, and team health. Answer Tip: Mention cycle time, lead time, escaped defects, team happiness, and sprint goal success. Explain why you choose specific metrics based on the team’s maturity. 🔹 3. How do you coach a team that’s doing Scrum only in name (ScrumBut)? Why they ask: Many teams adopt Scrum ceremonies without embracing Agile principles. Pro Tip: Talk about helping teams understand the “why” behind Scrum, running workshops, or improving cross-functional collaboration. 🔹 4. How do you facilitate remote or hybrid sprint events effectively? Why they ask: Remote work is still the norm in many industries in 2025. What to include: Tools (like Miro, Zoom, Mural, or Slack), time-boxing, rotating facilitators, and strategies for inclusive participation. 🔹 5. What’s the biggest mistake you made as a Scrum Master, and what did you learn? Why they ask: Self-awareness and growth mindset are critical. Answer Tip: Be honest. Reflect on what went wrong and how you handled it. This shows maturity and continuous improvement. 🔹 6. How do you handle a Product Owner who micromanages the team? Why they ask: Collaboration between PO and team can make or break productivity. What to say: Talk about facilitating boundary-setting conversations, clarifying roles, and encouraging trust-based collaboration. 🔹 7. How do you support a team that is consistently missing sprint goals? Why they ask: They want to see your coaching and problem-solving skills. Best approach: Explain how you might explore root causes (overcommitment, unclear stories, lack of focus), facilitate retrospectives, and help the team recalibrate expectations. 🔹 8. What’s your approach to handling team conflict? Why they ask: Conflict is normal. Interviewers want to know if you can manage it constructively. Answer Tip: Mention active listening, 1-on-1s, root cause analysis, and creating psychologically safe environments. 🔹 9. How do you balance servant leadership with delivery pressure from stakeholders? Why they ask: This question tests your leadership style and stakeholder management. What to say: Show that you protect the team’s focus, manage stakeholder expectations, and act as a bridge—not a barrier—between delivery and agility. 🔹 10. How do you stay up-to-date with Agile trends and practices? Why they ask: Continuous learning is key for any good Scrum Master. Pro Tip: Mention following thought leaders on LinkedIn, attending meetups, reading blogs (like Scrum.org, Agile Alliance), or completing certifications like PSM II or SAFe. Conclusion In 2025, being a Scrum Master is about more than frameworks and rituals. It’s about agile leadership, emotional intelligence, communication, and adaptability. Employers look for real-world experience, the ability to coach teams, and a mindset focused on continuous improvement. If you’re preparing for an interview, don’t just memorize answers — reflect on your real experiences. Interviewers want authenticity, not theory. Want more questions <<click here>>
Outcome Over Output – Focus on Value, Not Just Delivery

In today’s world, many companies are trying to move faster. Teams build and release new features, apps, or services more quickly than ever before. But here’s a key question: Are we actually making things better for the users or the business? That’s where the idea of “outcome over output” becomes important. What’s the Difference Between Output and Outcome? Output means the things a team creates or delivers — like a new website feature, a mobile app update, or a report. These are the actual products or tasks completed. Outcome means the results or impact of those outputs. In other words, what changed because of what we delivered? For example, if a team adds a new search feature to a website, that’s an output. But if that new feature helps users find products faster and increases sales, that’s the outcome. So, outputs are about doing, and outcomes are about achieving. Why Is Outcome More Important? When teams focus only on outputs, they may keep building things without checking if they’re useful or helpful. This can turn them into a “feature factory,” just adding more features without knowing if users actually need them. Focusing on outcomes helps teams: This leads to more meaningful work and better results. A Real-Life Example Imagine a team builds a chatbot to reduce customer support calls. They release the chatbot — that’s an output. But after a few weeks, they find out customers still call support because the chatbot is confusing. In this case, even though the team delivered something, it didn’t help reduce calls — the outcome was not achieved. This shows why simply delivering something isn’t enough. What truly matters is the result it creates. How to Focus on Outcomes To shift from output-focused to outcome-focused work, try these steps: Common Challenges Switching to outcome-based thinking isn’t always easy. Many teams are used to being measured by how much they do — like how many tasks they complete or how fast they work. Changing this mindset takes time and support from leaders. Teams also need the right tools and time to track outcomes and talk to users. In the beginning, it might feel slower. But in the long run, this approach helps teams build things that truly matter. Conclusion Today, speed is important — but value is even more important. Delivering a lot of features doesn’t mean much if they don’t help users or improve the business. By focusing on outcomes over outputs, teams can make sure they’re not just working hard, but also working smart. It’s about creating real impact, not just checking off tasks. Remember: Don’t just build more. Build what matters.
What Makes a Great Scrum Master (and What Doesn’t)

In Agile teams, the Scrum Master plays an important role. They help the team follow the Scrum process and make sure things run smoothly. But being a great Scrum Master is about much more than just organizing meetings. So, what makes someone truly great at this role? And what should they avoid? Let’s break it down. What Makes a Great Scrum Master 1. They Put the Team First A great Scrum Master is a servant leader. That means they don’t act like a boss. Instead, they support the team, help remove obstacles, and make sure everyone can do their best work. They focus on what the team needs — not what they want to control. 2. They Know Scrum Well (and Use It Wisely) A good Scrum Master understands the rules of Scrum — like how to run stand-ups, sprint planning, and retrospectives. But they also know that Scrum is just a tool. They use it in a smart way that fits the team, rather than following the rules blindly. 3. They Help Meetings Run Smoothly Instead of talking all the time or telling others what to do, a great Scrum Master facilitates meetings. That means they make sure everyone has a voice, the meetings stay focused, and the team gets the most out of each discussion. 4. They Protect the Team Outside distractions can slow a team down — like last-minute tasks from managers or interruptions during sprints. A great Scrum Master keeps those distractions away so the team can stay focused and finish what they planned. 5. They Coach and Guide The best Scrum Masters are also coaches. They help team members grow, teach Agile practices, support the Product Owner, and even help other departments understand how Scrum works. They make the whole organization better. What Doesn’t Make a Great Scrum Master 1. Being a Micromanager If a Scrum Master tries to control every detail or tells people how to do their jobs, it’s a problem. Scrum teams should organize their own work. A controlling Scrum Master slows the team down and lowers motivation. 2. Being a Rule Enforcer Some Scrum Masters focus only on rules and processes. They act like “Scrum police.” This doesn’t help teams grow or improve. A great Scrum Master explains why Scrum practices matter and helps the team use them in a helpful way. 3. Using the Same Approach for Every Team Every team is different. What works for one might not work for another. A great Scrum Master listens to the team and adjusts their style based on what the team needs. A one-size-fits-all approach doesn’t work in Agile. 4. Ignoring Stakeholders While focusing on the team is important, a Scrum Master also needs to work with others — like Product Owners, managers, and customers. A great Scrum Master builds good relationships outside the team to support communication and collaboration. 5. Not Growing or Learning Agile is all about learning and improving. A Scrum Master who isn’t learning new things or reflecting on how to improve may fall behind. Great Scrum Masters read, take courses, talk to other Agile professionals, and keep growing. In Conclusion A great Scrum Master supports the team, understands Scrum, handles problems quietly, and helps the team and organization grow. They don’t control the team — they empower them. They don’t just follow rules — they guide the team with purpose. A not-so-great Scrum Master might do too much, follow rules without thinking, or forget that people come first. If you’ve worked with a great Scrum Master, you know how valuable they are. If not — now you know what to look for.
Building Psychological Safety in Scrum Teams

In Scrum teams, success isn’t just about using the right tools or following the right steps. It’s also about making sure everyone on the team feels safe to share their thoughts, ideas, and even their mistakes. This feeling of safety is called psychological safety. When a team has it, everyone can do their best work. So, how can you build psychological safety in your Scrum team? Let’s break it down. What is Psychological Safety? Psychological safety means that team members feel okay speaking up. They don’t worry about being blamed, judged, or embarrassed if they share their opinions or if they make a mistake. This is really important for Scrum teams because Scrum is all about teamwork, talking openly, and learning from mistakes. If people feel unsafe to speak up, problems go unnoticed, and great ideas stay hidden. Why It’s Important in Scrum Scrum teams need to adapt and work together fast. Here’s why psychological safety helps: ✅ Better teamwork: Everyone can share what they know, so the team makes smarter choices.✅ Learning faster: Mistakes are seen as lessons, not failures.✅ More ownership: When people feel safe, they care more about the team’s success.✅ Happier teams: A safe, supportive environment makes people feel good about their work. Steps to Build Psychological Safety Here are simple things you can do to make your team feel safe: 1️⃣ Be a Role Model If you’re a Scrum Master, Product Owner, or team lead, show that it’s okay to not have all the answers. If you make a mistake or don’t know something, say so! This shows everyone that it’s normal to be honest and open. 2️⃣ Encourage Everyone to Speak In Scrum meetings like Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Reviews, and Retrospectives, make sure everyone has a chance to talk. Ask: This shows that everyone’s input matters. 3️⃣ Be Curious, Not Critical When someone shares an idea or concern, don’t jump in to judge or shut it down. Instead, ask questions to learn more: This way, people feel safe to keep sharing. 4️⃣ Celebrate Ideas and Learn from Mistakes Thank people when they share ideas, even if they’re small. Celebrate little successes, too. And if there’s a mistake, talk about what you learned from it—not who’s to blame. For example, in Retrospectives, ask “What can we learn from this?” instead of “Who made the mistake?” 5️⃣ Keep Checking In Psychological safety doesn’t happen overnight—it’s something to keep working on. Scrum Masters can ask in Retrospectives: This helps you keep improving as a team. The Scrum Master’s Job The Scrum Master has a big role in building psychological safety. They help protect the team from outside pressure, guide everyone to work together, and make sure all voices are heard. By showing kindness and curiosity, the Scrum Master helps build trust in the team. Conclusion Psychological safety isn’t just something nice—it’s needed for Scrum teams to succeed. When people feel safe to share, they come up with better ideas, help each other out, and make the team stronger. By leading by example, making sure everyone’s voice is heard, and talking about how the team can keep improving, you can build a safe and supportive Scrum team. And when your team feels safe, they’ll be ready to do their best work—together.
How to Move from Traditional Project Management to Agile

For years, project managers have used traditional methods—also known as Waterfall—to plan and run projects. These methods focus on following a step-by-step plan, with everything mapped out in advance. But today, businesses change quickly. That’s why Agile project management, which is more flexible and customer-focused, is becoming so popular. If you’re thinking about making the switch from traditional to Agile, here’s how to do it. 1. Understand the Differences First, it helps to see how the two approaches differ: The main change isn’t just in how you work—it’s in how you think. 2. Adopt an Agile Mindset Agile is more than a set of rules—it’s a new way of thinking: 3. Train Your Team A successful switch to Agile depends on everyone understanding how it works: 4. Start with a Small Project You don’t have to switch everything to Agile at once. Begin with a pilot project: 5. Use the Right Tools Agile uses different tools than traditional methods: 6. Keep Improving Agile isn’t a one-time change—it’s about always looking for ways to do better: 7. Involve Stakeholders Early In traditional projects, you might only talk to stakeholders at big milestones. Agile involves them more often: Conclusion Switching from traditional project management to Agile isn’t something you do overnight. It’s a journey of learning, adapting, and working together in new ways. By starting small, keeping things simple, and staying open to change, you’ll see how Agile can help you deliver better results, faster. In today’s world, that flexibility and focus on the customer can make all the difference.
The Future of Agile in Large Organizations

Agile started as a way for small software teams to move faster and create better products. But now, big companies with thousands of employees are trying to use Agile, too. This isn’t always easy—large organizations have lots of teams, managers, and processes that can slow things down. So, what does the future look like for Agile in these big companies? Let’s take a look. The Challenges of Doing Agile at Scale In smaller teams, Agile can work well because everyone is close and decisions happen quickly. But in big companies, there are many levels of managers and different departments. This can make it harder to bring Agile to life. One challenge is that people don’t always like change. Some managers are used to telling people exactly what to do. Agile, though, is about letting teams organize themselves and work together. This change can feel uncomfortable. That’s why making Agile work in large companies takes more than just new rules—it needs a new way of thinking. Scaling Frameworks: SAFe, LeSS, and More To help big companies use Agile, there are special frameworks designed for large teams: These frameworks can help, but they’re not magic. Each company has to adapt them to fit their own ways of working. Beyond IT: Agile for Everyone Agile isn’t just for software teams anymore. Big companies are using Agile in other departments, too—like marketing and HR. This helps everyone work together better and focus on customers. In the future, we’ll see Agile ideas—like working in small steps and getting feedback fast—spread throughout big companies. This can make the whole company faster and more flexible. Using Data and Technology New technology is also shaping the future of Agile. Tools like Jira or Trello help teams track their work and stay organized. But soon, data will play an even bigger role. For example, teams can look at data about how fast they’re working or where they’re getting stuck. This helps them improve and make better decisions. AI and automation might also help by handling boring tasks and showing where teams can speed up. Changing How Leaders Lead For Agile to really work in big companies, leaders need to change, too. In the past, leaders mostly told people what to do. Now, they need to focus on helping teams succeed—by removing obstacles and building trust. This new style of leadership is called servant leadership. Leaders who do this support their teams and help them do their best work. What’s Next? The future of Agile in big companies isn’t about using one single framework or tool. It’s about creating a culture where teams are always improving and thinking about what customers need. It’s about helping teams work well on their own and making sure everyone is moving in the same direction. Big companies that can truly embrace Agile will be able to move faster, make better products, and stay ahead of the competition. Conclusion Agile’s future in big companies looks promising—but it takes effort. Using the right frameworks, embracing data and technology, and focusing on teamwork and trust will make a real difference. When done well, Agile can become more than a process. It can become part of how the whole company works and grows.
Scrum Master Mistakes to Avoid: Common Anti-Patterns

Being a Scrum Master isn’t always easy. Even experienced Scrum Masters can fall into habits that seem helpful but actually hold the team back. These habits are called anti-patterns—they go against the purpose of Scrum. Let’s take a look at some common Scrum Master mistakes and how you can avoid them. 1. Being the Team’s Secretary What Happens:You end up scheduling meetings, writing notes, and updating task boards—all the time. Why It’s a Problem:The team becomes dependent on you and doesn’t learn to manage themselves. What to Do Instead:Let the team take ownership. Encourage them to update Jira and run parts of meetings. You’re there to guide, not to do everything. 2. Talking Too Much in Meetings What Happens:You lead every meeting, answer all questions, and fill every pause with your own input. Why It’s a Problem:Team members stop sharing ideas or speaking up. What to Do Instead:Ask open questions and let others lead. Stay quiet sometimes—give space for the team to think and talk. 3. Not Protecting the Team What Happens:Stakeholders interrupt the team, or urgent work gets pushed into the sprint at the last minute. Why It’s a Problem:The team loses focus and trust in the sprint plan. What to Do Instead:Say no to interruptions. Help the Product Owner push work to the next sprint. Explain why focus matters. 4. Micromanaging Like a Project Manager What Happens:You assign tasks or track who’s doing what. Why It’s a Problem:The team stops taking responsibility and starts waiting for direction. What to Do Instead:Let the team choose how to do their work. You support them by removing blockers and improving the process. 5. Ignoring Company-Wide Problems What Happens:You only focus on your team and don’t try to fix bigger issues. Why It’s a Problem:Bigger blockers like poor tools or cross-team delays slow down progress. What to Do Instead:Help fix problems beyond the team. Connect with other teams, raise issues, and push for system improvements. 6. Skipping Retrospectives What Happens:You cancel or rush retrospectives when the team is busy. Why It’s a Problem:The team misses chances to improve. What to Do Instead:Make retrospectives a priority. Use them to reflect, learn, and plan real changes—even small ones. 7. Staying the Same While the Team Grows What Happens:You do the same things each sprint, even when the team doesn’t need as much help. Why It’s a Problem:You stop adding value, and the team might outgrow your support. What to Do Instead:Adapt your role. Focus on coaching, mentoring, and helping other teams or the wider organization. Final Thoughts The Scrum Master’s job is to help the team grow, improve, and deliver value. But sometimes, doing too much—or not enough—can slow things down. By avoiding these common mistakes, you’ll become a better guide, coach, and leader. Keep learning, stay curious, and most importantly—listen to your team.
Creating a Learning Culture in Agile Teams

In today’s fast-moving world, learning should never stop—especially in tech and agile environments. The best teams are always growing, trying new things, and learning from each other. A strong learning culture helps teams stay up-to-date, motivated, and ready for whatever comes next. Let’s look at how teams are making learning a regular part of their work—and why it matters. 1. Learning Sprints: Quick and Focused Learning Agile teams are now setting aside time for short “learning sprints.” These are planned sessions where the whole team focuses on learning a new tool, skill, or concept together. Instead of waiting for formal training, teams learn what they need right away—whether it’s a coding language, a new design pattern, or a DevOps tool. Why it works: 2. Tech Radar Meetings: Tracking What’s New Many teams now hold regular tech radar meetings. This is where they look at new tools, technologies, or trends and decide whether to try, adopt, or avoid them. It’s a smart way to stay informed, avoid tech debt, and make better technology choices. Why it works: 3. Internal Conferences and Demos Big companies often host their own internal conferences, lightning talks, or demo days. These events are a chance for team members to share what they’ve learned, show cool projects, or teach others something new. It’s like having your own tech event—right inside the company. Why it works: 4. Creating the Right Environment: Safety and Trust A learning culture only works when people feel safe and respected. Team members should feel free to ask questions, share ideas, or admit they don’t know something—without fear of being judged. That’s called psychological safety, and it’s key to helping people grow. Also, when teams have autonomy, they can choose how and what they learn. This gives them ownership and makes learning more fun and meaningful. Why it works: Why Learning Culture Matters When teams keep learning, the whole company benefits: Conclusion Creating a learning culture doesn’t need to be complex. Start small—add learning sprints, host tech talks, and make time to explore new ideas. Give your team the freedom and safety to learn, and you’ll build a workplace where growth never stops.
How PSPO Certification Boosts Your Product Management Career

Introduction Product management is a fast-growing field, and companies are adopting Agile methods more than ever. To stay ahead, product managers need the right skills and certifications. One of the best-known certifications in Agile is the Professional Scrum Product Owner (PSPO) certification from Scrum.org. The PSPO certification proves that you understand Scrum principles, stakeholder management, and value-based product development. Whether you’re starting in product management or looking to grow your career, this certification can be a game-changer. Let’s explore how PSPO certification can help you become a better product manager and boost your career. 1. Helps You Understand Agile and Scrum Agile development is widely used, and Scrum is one of its most popular frameworks. The PSPO certification teaches you the key Scrum concepts, such as backlog management, stakeholder collaboration, and delivering value incrementally. This helps you align your work with Agile practices, making your product development process more effective. 2. Increases Your Job Opportunities Product management is competitive, and employers look for certified professionals who can apply Agile methods effectively. The PSPO certification makes your resume stand out and shows that you understand Scrum and product ownership. Many companies—especially in tech, healthcare, finance, and retail—prefer hiring certified professionals who can manage Agile teams and lead products successfully. Having this certification can open doors to better job opportunities and higher salaries. 3. Improves Decision-Making and Prioritization One of the biggest challenges in product management is deciding what to work on first. The PSPO certification teaches you how to prioritize tasks based on customer needs and business goals. You’ll learn about Value-Based Prioritization, MoSCoW, and other techniques that help you decide what features and updates will bring the most value. This ensures that your team works on the right things at the right time. 4. Enhances Your Communication With Stakeholders Product managers work with different groups—customers, developers, marketers, and company leaders. The PSPO certification helps you improve your stakeholder communication skills, making it easier to align everyone toward a common goal. You’ll learn how to: These skills help you build strong relationships and ensure that your product meets both business and customer needs. 5. Helps You Deliver More Business Value Being a great product manager is not just about managing a backlog—it’s about delivering real business value. The PSPO certification teaches you how to: With these skills, you can contribute directly to your company’s success and become a more strategic leader in your organization. 6. Supports Long-Term Career Growth The PSPO certification isn’t just about passing an exam—it helps you develop a growth mindset and continuously improve your skills. It can lead to higher positions, such as Senior Product Owner, Product Manager, Head of Product, or even Chief Product Officer (CPO). Additionally, if you want to deepen your knowledge, you can go for advanced certifications like PSPO II and PSPO III, which focus on more advanced product management techniques. Conclusion In today’s Agile-driven world, the PSPO certification is a powerful tool for product managers. It helps you understand Agile, improve decision-making, communicate better with stakeholders, and increase job opportunities. If you’re looking for a way to boost your career, earn more, and become a better product leader, getting PSPO-certified is a smart investment. You can join our session to take the next step and unlock new career possibilities with the PSPO certification!
Focus on sustainability and social responsibility in agile teams

Why Sustainability and Social Responsibility Matter In today’s world, businesses need to think about more than just profits. They must also consider how their work impacts the environment and society. Agile teams, known for their flexibility and efficiency, are now integrating sustainability and social responsibility into their workflows. This blog explores how Agile methods can support these values, the challenges teams may face, and best practices to create a positive impact. Why Sustainability and Social Responsibility Are Important Sustainability means meeting today’s needs without harming future generations. Social responsibility involves making ethical choices that benefit society. Climate change, pollution, and social inequality are growing concerns, making it necessary for businesses to step up. Agile teams work in short cycles, making them well-suited to adopt sustainable and ethical practices. By doing so, they help protect the environment, improve workplace ethics, and contribute to corporate social responsibility (CSR). How Agile Teams Support Sustainability and Social Responsibility 1. Improving Practices Over Time Agile is all about continuous improvement. Teams can gradually add sustainable practices, evaluating their impact at every stage. For example, software teams can write energy-efficient code to lower the carbon footprint of digital products. 2. Minimizing Waste Scrum, Kanban, and other Agile methods focus on efficiency and reducing waste. By cutting down on unnecessary documentation, optimizing resources, and eliminating excess meetings, Agile teams can operate more sustainably. 3. Remote Work Reduces Carbon Footprint Many Agile teams work remotely, reducing pollution from commuting and office energy use. Digital collaboration tools help maintain productivity while lessening the environmental impact. 4. Making Ethical Choices Agile teams can factor ethics into their decisions, ensuring products and services benefit society. This can mean developing accessible software, promoting diversity, or working with ethical suppliers. 5. Aligning with Stakeholders for a Greater Impact Close collaboration with customers and partners allows Agile teams to align their work with sustainability goals. This could involve creating eco-friendly products or supporting fair trade initiatives. Challenges of Implementing Sustainable Agile Practices Despite the benefits, Agile teams may face challenges: Best Practices for Agile Teams To successfully integrate sustainability and social responsibility, Agile teams can follow these steps: Conclusion Sustainability and social responsibility are becoming essential for long-term business success. Agile teams, with their ability to adapt and improve, are in a great position to lead the way. By minimizing waste, making ethical decisions, and promoting sustainability, Agile teams can contribute to a better world while still delivering high-quality products and services. As businesses recognize the importance of these values, Agile methods will continue evolving to make a positive impact on society and the planet.
Understanding Flow Metrics in Agile

Agile teams aim to work efficiently and deliver value quickly. Traditional metrics like velocity only measure the speed of work, but they don’t highlight inefficiencies in the workflow. This is where flow metrics come in. Flow metrics track how work moves through a process, helping teams spot delays and improve productivity. Three key flow metrics—Flow Efficiency, Cycle Time, and Throughput—help teams understand and optimize their workflow. Using these, Agile teams can work smarter, remove bottlenecks, and improve delivery speed. What Are Flow Metrics? Flow metrics measure how smoothly work progresses, revealing hidden delays and inefficiencies. Unlike traditional Agile metrics, which focus on estimated progress, flow metrics provide real-time insights into work completion. 1. Flow Efficiency Flow efficiency shows how much time is spent actively working on a task versus waiting. It is calculated as: Flow Efficiency=(Active Work TimeTotal Cycle Time)×100\text{Flow Efficiency} = \left( \frac{\text{Active Work Time}}{\text{Total Cycle Time}} \right) \times 100 A low percentage means too much time is wasted waiting, while a higher number shows a more efficient workflow. 2. Cycle Time Cycle time measures how long it takes to complete a task from the moment work starts. Cycle Time=Completion Date−Start Date\text{Cycle Time} = \text{Completion Date} – \text{Start Date} A shorter cycle time means tasks are completed faster. If cycle time increases, it signals delays in the workflow. 3. Throughput Throughput measures how many tasks are completed in a given timeframe. Throughput=Total Work Items Completed in a Given Time Frame\text{Throughput} = \text{Total Work Items Completed in a Given Time Frame} Consistently high throughput indicates a well-optimized process, while fluctuations may show workflow issues. Why Flow Metrics Matter in Agile Traditional Agile metrics don’t always reveal the reasons behind delays. Flow metrics help teams: How to Improve Agile Workflows with Flow Metrics Conclusion Flow metrics—Flow Efficiency, Cycle Time, and Throughput—help Agile teams work more effectively. By focusing on real-time workflow data instead of just speed, teams can identify and fix inefficiencies, making their processes smoother and more predictable. By applying these metrics, organizations can build a stronger Agile foundation, improving team performance and delivering value to customers faster.
Scrum Masters Transitioning into Agile Coaches

The role of Scrum Masters is evolving. They are no longer just responsible for managing Scrum events and team workflows. Instead, they are taking on broader responsibilities, becoming Agile Coaches who help entire organizations embrace Agile principles. This shift is happening because businesses need Agile thinking not just in development teams but across leadership and different departments. As a result, the demand for Agile Coaches is increasing, making it a great opportunity for Scrum Masters to expand their influence. Understanding the Role of a Scrum Master Scrum Masters have traditionally worked with teams to implement Scrum effectively, facilitating sprint planning, daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives. Their main job is to remove obstacles and improve teamwork. However, as Agile adoption grows, organizations need a more strategic approach, which is where Agile Coaches come in. The Shift from Scrum Master to Agile Coach Agile Coaches operate on a larger scale. While Scrum Masters focus on individual teams, Agile Coaches work across an entire organization, helping leadership and different departments adopt Agile ways of working. This shift is not just about managing multiple teams but about fostering a cultural change within the company. Key Differences Between a Scrum Master and an Agile Coach Why Businesses Need Agile Coaches As organizations grow, Agile adoption must go beyond individual teams. Agile Coaches help: How to Transition from Scrum Master to Agile Coach If you’re a Scrum Master looking to become an Agile Coach, here are some key steps to take: The Future of Agile Coaching As Agile expands beyond software development into areas like marketing, finance, and HR, the role of Agile Coaches will continue to grow. Companies need Agile Coaches to guide them through this transformation, embedding Agile principles into their culture. This creates an exciting career path for Scrum Masters who want to expand their influence. Conclusion The role of Scrum Masters is changing, and Agile Coaching is the next step. Companies need Agile leadership at all levels, making this transition an excellent opportunity. By developing the right skills, Scrum Masters can take on a more strategic role and help organizations fully embrace Agile. Becoming an Agile Coach means not just helping teams follow Agile, but helping businesses truly live it.
Simple Guide to Scaling Agile for Large Teams and Complex Projects

As companies grow and handle bigger projects, scaling Agile becomes essential. While Agile works great for small teams, larger organizations face challenges in staying coordinated, aligned, and productive. Frameworks like Scrum of Scrums help multiple teams work together while staying aligned with company goals. Let’s explore key strategies and benefits of scaling Agile practices. Why Scale Agile Practices? Agile was designed for small teams, but as projects and organizations grow, challenges arise. Some common challenges include: Scaling frameworks help overcome these challenges by improving communication and aligning goals. Popular Frameworks for Scaling Agile There are several ways to scale Agile effectively. Here are three popular frameworks: 1. Scrum of Scrums (SoS) Scrum of Scrums extends the traditional Scrum framework to coordinate multiple teams. Key Features: How It Works: 2. SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) SAFe provides a structured way to scale Agile across large companies. Key Features: 3. LeSS (Large-Scale Scrum) LeSS keeps Scrum simple while applying it to bigger teams. Key Features: Benefits of Scaling Agile Scaling Agile offers many benefits for organizations: Best Practices for Scaling Agile To successfully scale Agile, follow these best practices: Conclusion Scaling Agile frameworks like Scrum of Scrums, SAFe, and LeSS help organizations stay flexible and efficient, even as they grow. By focusing on collaboration, goal alignment, and best practices, companies can navigate the challenges of scaling Agile and achieve long-term success.
Simple Agile Best Practices for Better Project Management

Agile is a popular way to manage projects because it helps teams adapt quickly, collaborate better, and deliver results faster. But just following Agile isn’t enough—using the right best practices is essential for success. Here are some simple and effective tips to help Agile teams work smarter, produce better products, and stay on track. 1. Work as a Team: Developers and Testers Together In the past, developers and testers worked separately, which caused delays and communication problems. Agile encourages them to collaborate from the start. Tips: This teamwork approach helps finish tasks faster and with fewer mistakes. 2. Focus on Quality from the Beginning Quality isn’t just the job of the QA (Quality Assurance) team; it’s everyone’s responsibility. Waiting until the end to test products causes delays and problems. Tips: These practices help teams deliver better products without slowing down. 3. Use Continuous Integration and Delivery (CI/CD) CI/CD means constantly integrating code changes and delivering updates to users quickly. This approach reduces risks and makes it easier to fix problems. Tips: CI/CD makes it easier for teams to deliver features and fixes faster. 4. Plan Sprints and Refine Backlogs Regularly Good planning keeps Agile teams focused and productive. Sprint planning and backlog refinement are key for clear priorities. Tips: These practices help teams stay organized and aligned with business goals. 5. Keep Improving Agile teams need to keep learning and improving through regular feedback. Tips: Continuous improvement helps teams stay competitive and effective. Conclusion Following these simple Agile best practices can help teams work better, deliver high-quality products, and meet goals efficiently. By focusing on teamwork, quality, automation, planning, and improvement, organizations can unlock the full benefits of Agile and achieve long-term success.
Remote Agile Teams: Making Scrum Work in a Distributed Environment

Remote work has become common in today’s global world. While Agile focuses on teamwork, flexibility, and regular communication, it can be tricky to do Scrum with a remote team. But with the right approach, Scrum can still work well for distributed teams. Let’s see how to make it happen. Challenges of Remote Scrum Doing Scrum remotely comes with its own set of challenges: Tips to Make It Work Here are some ways to overcome these challenges and make remote Scrum successful: 1. Use the Right Tools Good tools are essential for remote teams. Some useful ones include: Make sure everyone knows how to use these tools to avoid confusion. 2. Use Asynchronous Communication When team members are in different time zones, asynchronous communication is key. You can: 3. Adapt Scrum Meetings Scrum ceremonies are important for teamwork. Here’s how to adjust them: 4. Build Team Culture To keep the team connected and motivated, try these: 5. Focus on Transparency Being open about work is crucial for remote teams. You can: Tips for Remote Scrum Masters Scrum Masters play a key role in keeping the team aligned. Here’s what they can do: Leadership Support for Remote Teams Leaders play a big part in helping remote Scrum teams succeed. They should: Conclusion Remote work is here to stay, and Agile teams can adapt to this new reality. By using the right tools, building strong team connections, and keeping communication clear, Scrum can work just as well for remote teams. The key is to stay flexible, be transparent, and keep improving. With these principles, remote Scrum teams can achieve great results, no matter where their members are.
Continuous Learning and Development for Scrum Practitioners

Scrum and Agile methods are always changing, which means Scrum practitioners need to keep learning to stay effective. As markets and technology evolve, staying updated with new practices and tools is crucial for success. Let’s explore why continuous learning is important, the benefits it offers, and how Scrum practitioners can keep growing. Why Continuous Learning is Important Scrum is more than just a framework; it’s a mindset. Staying open to learning helps Scrum practitioners: What to Focus on for Growth To grow, Scrum practitioners can focus on several key areas: Ways to Keep Learning There are many ways Scrum practitioners can keep improving: How Organizations Can Help Organizations play a big role in helping their teams grow. They can: Benefits of Continuous Learning For Scrum practitioners and organizations, continuous learning brings many benefits: Conclusion Continuous learning is essential for Scrum practitioners. By taking certifications, exploring new tools, and staying curious, practitioners can stay ahead in their field. Organizations that support their teams’ growth also gain long-term benefits. Keep learning, and success will follow! Ready to take your Scrum skills to the next level? Explore our recommended courses and resources today!
Challenges in Scrum Implementation: How to Solve Them

Scrum is a popular Agile framework that helps teams manage complex projects. But using Scrum successfully isn’t always easy. Many organizations face challenges that can slow them down or cause confusion. Let’s look at some common problems in Scrum and simple ways to fix them. Common Problems in Scrum Easy Fixes for Scrum Challenges Real-Life Stories Conclusion Scrum can bring great results, but it comes with challenges. By addressing common issues like poor communication, resistance to change, and unclear roles, teams can unlock Scrum’s full potential. Success with Scrum requires training, teamwork, and a willingness to adapt. With these steps, organizations can make Scrum work for them and achieve their goals.Scrum is a popular Agile framework that helps teams manage complex projects. But using Scrum successfully isn’t always easy. Many organizations face challenges that can slow them down or cause confusion. Let’s look at some common problems in Scrum and simple ways to fix them.
Focusing on Value Stream Management: Making Work More Efficient

In today’s fast-changing business world, companies want to work smarter and give their customers the best value. One way to do this is by using Value Stream Management (VSM). This method helps businesses understand and improve the steps they take to create products or services, making everything run smoother and faster. What is Value Stream Management? Value Stream Management is a way to see, analyze, and improve how value flows through a company’s processes. A value stream includes every step, from coming up with an idea to delivering the final product or service. VSM focuses on cutting out wasted time and effort while making sure every step helps meet customer needs. Why is Value Stream Management Important? Companies are using VSM because it helps them in many ways: How to Use Value Stream Management To make the most of VSM, companies follow these steps: Tools and Techniques for VSM Businesses use different tools to support VSM, such as: Examples of Value Stream Management Challenges in Using VSM While VSM is helpful, companies may face challenges like: Conclusion Value Stream Management is a powerful way for companies to work more efficiently and provide greater value to customers. By improving workflows, reducing waste, and encouraging teamwork, VSM helps businesses stay competitive. It’s a smart strategy that benefits both the company and its customers.
Scrum in Education: A New Way to Learn and Work Together

Scrum, a popular method used in software development, is now being introduced in schools and colleges. It helps students work better as a team, take responsibility for their tasks, and build good study habits. Let’s see how Scrum is making learning more effective and enjoyable. What is Scrum? Scrum is a way of working that focuses on teamwork and completing tasks in short time frames called sprints. It uses specific roles like the Scrum Master (who guides the team) and the Product Owner (who sets goals). Daily check-ins and regular feedback are key parts of Scrum, making it a good fit for learning environments. Why Use Scrum in Education? Teachers and students face challenges like poor teamwork, missed deadlines, and ineffective study methods. Scrum helps solve these problems by: How Does Scrum Work in Education? Scrum is adapted to fit the needs of students and teachers. Here’s how it’s done: Examples of Scrum in Action Benefits for Students Challenges and How to Handle Them Conclusion Scrum is not just a new way to manage tasks—it’s a tool that helps students learn essential skills like teamwork, responsibility, and time management. By using Scrum, schools and colleges can make learning more effective and enjoyable. It’s a simple change with big benefits for both students and teachers.
Using Fun Activities to Learn Agile Principles

Agile is a popular way of managing projects and creating software. However, it can be tricky for beginners to fully understand how it works. That’s where fun activities and hands-on games come in. These methods make learning Agile easier and more enjoyable while helping teams work better together. Why Activities Work for Agile Learning Traditional teaching methods like lectures and reading might not show how Agile works in real life. Interactive activities are different. They put learners in situations that feel like real Agile environments. This way, participants can learn by doing. Agile values teamwork and communication. Activities reflect these values by focusing on people working together and solving problems. They also help learners remember concepts better than just reading or listening. Popular Games and Activities for Agile Benefits of Hands-On Agile Training How to Use Activities in Training Organizations can add these games to workshops or team-building sessions. Agile coaches or Scrum Masters can lead the activities, adjusting them to suit the team’s experience level. After each activity, it’s essential to talk about what the team learned and how it applies to their work. This helps connect the activity to real Agile projects. Conclusion Interactive activities and games are changing the way people learn Agile. They make learning fun, practical, and memorable. These methods also help teams work better together and adapt to Agile practices. As more companies adopt Agile, using these creative training tools can help teams succeed and grow.
Scrum in a Remote/Hybrid World

The way teams work has changed, with remote and hybrid setups now common. These changes bring new challenges for Scrum teams that rely on collaboration, communication, and transparency. Luckily, Scrum’s flexible nature makes it easy to adapt to these new ways of working. Here are simple ways Scrum teams can succeed in a remote or hybrid world, along with tools and tips to stay productive and engaged. 1. Adjusting Daily Stand-Ups for Remote Teams Daily stand-ups keep teams aligned, but they can be tricky with time zones and technology issues. Video tools like Zoom or Microsoft Teams work well for live meetings, keeping communication clear. For teams in different time zones, tools like Slack or Standuply let members share updates asynchronously. This ensures everyone stays informed without needing to meet at the same time. 2. Virtual Sprint Planning and Backlog Refinement Remote sprint planning can be as effective as in-person sessions with the right tools. Platforms like Jira, ClickUp, or Trello help teams prioritize tasks and assign work. Shared screens and online whiteboards like Miro or MURAL make planning interactive. Clear documentation and equal participation ensure everyone stays involved. 3. Improving Communication Good communication is even more important for remote or hybrid teams. Tools like Slack, Microsoft Teams, or Discord keep conversations organized and accessible. Regular check-ins, clear documentation, and setting expectations for response times help teams stay aligned and avoid miscommunication. 4. Using Tools for Collaboration Technology helps remote teams collaborate easily. Tools like Confluence for documentation, GitHub for coding, and Figma for design ensure everyone can work together, no matter where they are. Real-time tools like Google Workspace or Notion allow teams to share updates and track progress seamlessly, keeping everyone on the same page. 5. Making Retrospectives Engaging Remote retrospectives can feel less personal. Interactive tools like Retrium or Parabol make them more dynamic by offering templates and visual aids. Encourage open sharing and try different formats to keep retrospectives fresh and meaningful. 6. Boosting Team Morale Remote work can feel isolating, which affects morale. Virtual team-building activities, like online games or coffee chats, help teams stay connected. Tools like Officevibe or TeamMood can track team sentiment, helping Scrum Masters address concerns early and create a supportive environment. 7. Tracking Progress and Delivering Results It’s important to keep track of work in remote Scrum. Dashboards from tools like Jira or Monday.com provide real-time progress updates. Automated reports keep stakeholders informed without extra meetings. Focusing on clear sprint goals ensures teams deliver value and stay aligned with priorities. 8. Managing Time Zone Challenges For teams in different time zones, overlapping hours are key for important meetings like sprint planning. For other work, tools like Loom for video updates or Notion for documentation help teams stay connected. Flexibility and understanding make it easier for distributed teams to work efficiently without burning out. Conclusion: Scrum is perfect for remote and hybrid work because of its adaptability. Using the right tools, improving communication, and focusing on team morale helps Scrum teams overcome the challenges of working remotely. As remote work evolves, so will Scrum practices and tools. Teams that embrace these changes will thrive, delivering great results while staying collaborative and innovative in any setup.
AI-Powered Scrum Tools

Scrum has changed how teams work together to deliver projects, especially in software development. By focusing on short-term goals, flexible planning, and ongoing improvement, Scrum helps teams work more efficiently. Now, artificial intelligence (AI) is making Scrum even better by offering tools that help predict problems, assign tasks, and make smarter decisions. Here, we’ll look at how AI-powered tools improve Scrum, including predictive analytics, smart task assignment, and more. 1. Predictive Analytics: Planning Ahead AI tools with predictive analytics give teams useful insights into how projects are going. These tools analyze past data, team performance, and current trends to predict issues like delays or resource shortages. For example, tools like Jira Advanced Roadmaps use AI to estimate how long tasks will take, highlight task dependencies, and create better sprint plans. This helps Scrum Masters and Product Owners fix problems early and keep the team on track. AI also helps assess risks. It can point out potential issues like underestimated tasks or overloaded team members, making it easier to adjust plans. 2. Smart Task Assignment: Working Smarter Assigning tasks in Scrum means balancing workloads, skills, and availability. AI tools make this easier by analyzing team members’ skills and past work to suggest the best task assignments. For example, tools like Trello with Butler AI can recommend who should handle specific tasks based on their expertise. Similarly, GitHub Copilot can suggest the best contributors for certain coding tasks. This saves time and ensures everyone is working on tasks that match their skills, boosting productivity. 3. Better Sprint Planning AI makes sprint planning faster and more accurate by automating backlog prioritization and effort estimation. AI tools rank tasks based on factors like customer impact and technical dependencies. Tools like ClickUp’s AI Assistant can even create draft sprint plans that match the team’s capacity. This reduces time spent in meetings while keeping plans reliable and effective. 4. Real-Time Tracking and Reporting Tracking progress and creating reports can take a lot of time. AI tools make this easier by offering real-time updates and automatic reports. These tools keep everyone informed and highlight any deviations from sprint goals. For instance, Monday.com uses AI to create live dashboards that show project progress and suggest solutions to problems. Automated reports save time for Scrum Masters, letting them focus on team collaboration. 5. Improved Communication and Teamwork AI tools help teams communicate and collaborate better. AI chatbots integrated with tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams can answer questions, remind team members about tasks, or even run virtual stand-ups. For example, Standuply’s AI Assistant collects updates from team members and summarizes them. This saves time and ensures everyone stays on the same page, even in different time zones. 6. Understanding Team Morale Team morale is key to Scrum success. AI tools with sentiment analysis can monitor team communication to understand how everyone is feeling and spot signs of burnout or frustration. Tools like TeamMood or Officevibe analyze team sentiment and provide feedback. Scrum Masters can use this information to address issues early, creating a happier and more productive team environment. 7. Smarter Retrospectives AI improves Scrum retrospectives by identifying trends in team performance and offering actionable suggestions. Tools like Parabol analyze sprint data to highlight what went well and what needs improvement. This helps teams learn from each sprint and continuously improve their workflow. Conclusion: The Future of AI in Scrum AI is changing how Scrum teams work, making processes faster, smarter, and more collaborative. From smarter task assignment to better morale tracking, AI-powered tools help teams achieve better results with less effort. As AI evolves, its role in Scrum will only grow. Teams that embrace these tools will stay ahead, delivering high-quality work while fostering a culture of improvement and adaptability. Adopting AI tools isn’t just a step forward—it’s a leap into the future of teamwork.
Agile in Non-IT Sectors: Applying Agile Principles

Agile is often associated with software development, but its principles can be applied to many other fields, like marketing, finance, and healthcare. By focusing on flexibility, teamwork, and customer satisfaction, Agile is helping different industries work more effectively and adapt to changes faster. What is Agile? Agile is a way of working that prioritizes people, collaboration, and quick responses to change. Instead of sticking to rigid plans, Agile teams break big projects into smaller tasks and work on them step by step. This makes it easier to adjust to new information and deliver results that matter to stakeholders. Marketing: Flexible Strategies for Fast-Changing Markets Marketing is a fast-moving field where trends and customer preferences change quickly. Agile marketing helps teams respond to these changes effectively by using short-term planning and regular check-ins. This approach helps: For example, a content team can use Agile to plan, create, and share content in short cycles. Regular reviews help them see what works and adjust their approach. Finance: Smarter Planning and Risk Management Finance is often seen as a rigid field, but Agile can make it more flexible. Finance teams can use Agile to manage risks, improve forecasts, and allocate resources more effectively. They can: Many finance teams use tools like Kanban boards to track progress and keep everyone on the same page. Healthcare: Better Care Through Teamwork Healthcare is a complex field with constant demands. Agile helps improve patient care and streamline operations by focusing on collaboration and adaptability. Key benefits include: For instance, hospitals can use Agile to manage projects like introducing new health record systems or launching public health programs. Challenges of Using Agile Outside IT Adopting Agile in non-IT fields comes with challenges: To overcome these challenges, organizations need to focus on change management, provide training, and adapt Agile practices to suit their specific needs. Conclusion Agile’s focus on flexibility and delivering value makes it useful in many fields beyond IT. Whether it’s creating better marketing campaigns, improving financial planning, or enhancing patient care, Agile helps teams work more efficiently and adapt to change. By adopting Agile principles, non-IT industries can boost collaboration, innovation, and success in today’s fast-changing world.
Business Agility: Staying Flexible, Adaptable, and Ready for Change

In today’s fast-changing world, businesses face new challenges and opportunities every day. With new technologies, shifting customer expectations, and global market changes, companies need more than just efficiency to succeed. They need business agility—the ability to adapt, respond, and thrive in any situation. What is Business Agility? Business agility means more than just following agile methods in software development. It’s about building a flexible and adaptive organization. It focuses on creating a culture where quick decisions, learning, and innovation happen across the company. Key parts of business agility include: Why Business Agility is Important Organizations that adopt business agility enjoy several benefits: How to Become More Agile Becoming an agile business takes effort and planning. Here are some steps to get started: Examples of Business Agility Here are a few companies showing the power of agility: The Future of Business Agility As the world keeps changing faster, agility will be essential for success. Businesses must see agility as an ongoing process, not a one-time effort. This means constantly evaluating, improving, and building a culture of resilience and innovation. In summary, business agility is key to surviving and thriving in an unpredictable world. By staying flexible, adaptable, and responsive, companies can handle uncertainty, seize new opportunities, and secure long-term success.
Simplifying SAFe® DevOps

In today’s fast-moving world, businesses need to deliver high-quality software quickly. To make this happen, teams must work together better and streamline their processes. SAFe® DevOps provides a clear way to connect development (Dev) and operations (Ops) teams, helping them deliver software faster, more efficiently, and with fewer issues. What is SAFe DevOps? SAFe DevOps is a part of the Scaled Agile Framework® (SAFe), designed to bring development and operations teams together. It focuses on improving teamwork, automating processes, and speeding up how software moves from an idea to a finished product. The goal is to break down barriers between teams and ensure everyone works toward delivering value to customers. Key Features of SAFe DevOps Benefits of SAFe DevOps How to Start with SAFe DevOps Challenges in SAFe DevOps Switching to SAFe DevOps isn’t always easy. Teams might resist change, silos can be hard to break, and automating old systems can be tricky. However, with good leadership, training, and a focus on continuous improvement, these challenges can be overcome. Conclusion SAFe DevOps combines the agility of DevOps with the scalability of SAFe, making it perfect for large organizations. It helps teams work together better, deliver software faster, and respond quickly to customer needs. By adopting SAFe DevOps, businesses can stay competitive and deliver value efficiently in today’s fast-paced world.
Why Emotional Intelligence is Essential for Agile Leaders

In today’s fast-changing world, agile leaders play a key role in helping teams adapt, innovate, and succeed. While technical skills and strategic thinking are important, emotional intelligence (EI) is what truly sets great agile leaders apart. EI helps leaders understand and manage emotions—their own and others’—to build strong relationships and create positive team environments. What is Emotional Intelligence? Emotional intelligence, or EQ, is the ability to recognize and control emotions and handle relationships effectively. It includes five main skills: self-awareness, self-control, motivation, empathy, and good social skills. These abilities align perfectly with agile leadership, where collaboration, adaptability, and communication are essential. Why Agile Leaders Need Emotional Intelligence 1. Building Trust and Safe Spaces Trust is critical in agile teams. When team members feel safe to share ideas or voice concerns, they work better together. Leaders with emotional intelligence create this trust by being self-aware of their actions and empathetic to others’ feelings. This makes team members feel valued, encouraging creativity and teamwork. When people trust their leader, they’re more open to trying new things without fear of failure. 2. Handling Change and Uncertainty Agile environments are full of change. Leaders with strong EI stay calm and focused during uncertainty, thanks to their ability to regulate their emotions. They also understand their team’s concerns and provide encouragement, helping everyone stay positive and focused on solutions. This stability allows teams to adapt and overcome challenges more effectively. 3. Improving Team Collaboration Collaboration is at the heart of agility, and emotionally intelligent leaders excel at bringing people together. With strong communication and conflict resolution skills, they ensure teams work in harmony. By listening to everyone and valuing different viewpoints, these leaders create an inclusive environment where every voice matters. This boosts creativity and leads to better ideas and solutions. 4. Encouraging Feedback and Growth Continuous improvement is a key part of agile practices, and feedback is vital for growth. Leaders with high emotional intelligence know how to give feedback in a constructive and motivating way. Self-awareness helps them avoid being overly critical, while empathy ensures they deliver feedback thoughtfully. This approach makes team members more open to learning and improving, benefiting the entire team. 5. Boosting Motivation and Engagement Engaged and motivated teams perform better. Agile leaders with strong EI know what drives their team members and help connect their goals with the organization’s vision. By showing empathy and communicating clearly, they create a sense of purpose and excitement about the work. This not only improves productivity but also makes the workplace more enjoyable for everyone. How to Build Emotional Intelligence The good news is that emotional intelligence can be learned and developed. Here are some ways agile leaders can improve their EI: Conclusion Emotional intelligence is a must-have skill for agile leaders. It helps them build trust, handle change, and foster collaboration, creating a strong foundation for team success. By improving their EI, leaders can create positive environments where teams thrive, adapt, and achieve great results together.
Challenges of Scaling Agile and How to Overcome Them

Agile has changed how teams work by encouraging flexibility, collaboration, and continuous improvement. While it works great for small teams, applying Agile across a large organization can be challenging. Scaling Agile requires more than just using Agile practices—it needs a change in mindset, processes, and coordination across different teams. Here are some common challenges and tips on how to handle them. 1. Cultural Resistance One of the main obstacles is the company’s culture. Traditional businesses often follow strict hierarchies and processes that don’t fit well with Agile’s focus on teamwork, transparency, and flexibility. How to Overcome: 2. Inconsistent Practices Between Teams Different teams may adopt different Agile methods—some use Scrum, others Kanban—causing confusion and inefficiency across the organization. How to Overcome: 3. Communication and Coordination Problems When Agile expands to multiple teams, communication can become tricky. Miscommunication and a lack of visibility across teams can slow down progress. How to Overcome: 4. Managing Dependencies and Priorities As more teams get involved, dependencies between tasks can pile up, making it hard to prioritize and deliver work efficiently. Teams might get stuck waiting for others, causing delays. How to Overcome: 5. Resistance to Change Some people might resist Agile because they fear losing control or are unsure about the new way of working. This resistance can come from managers or other key stakeholders. How to Overcome: 6. Measuring Success Traditional metrics like hours worked or tasks completed don’t show how well Agile teams are performing. Without the right metrics, it’s hard to know if things are improving. How to Overcome: Conclusion Scaling Agile is not always easy, but it can bring huge benefits if done right. By addressing cultural resistance, standardizing practices, improving communication, managing dependencies, and using the right metrics, organizations can successfully expand Agile across their teams. The key is to stay flexible, encourage collaboration, and keep improving. With the right approach and dedication, Agile can drive innovation and help businesses succeed on a larger scale.
What is Scrum? A Simple Guide for Beginners

Scrum is a popular way for teams to work together on projects, especially when things can get complicated. Originally created for software development, it’s now used in many fields like marketing, design, and even construction. Scrum helps teams work faster, stay organized, and deliver results step by step. The name “Scrum” comes from rugby, where players huddle together to move the ball forward. In the same way, Scrum teams collaborate closely to reach their goals. How Does Scrum Work? Scrum breaks big projects into smaller tasks that can be done in short periods of time, called Sprints. This helps teams stay focused and adjust quickly when things change. Key Ideas of Scrum Scrum Roles: Who Does What? Scrum Tools (Artifacts) Scrum Meetings (Events) Why Use Scrum? Conclusion Scrum is a simple yet powerful way for teams to work together, especially on complex projects. By breaking work into smaller chunks, staying in constant communication, and adapting when needed, teams can deliver better results faster. Whether you’re in software, marketing, or any other industry, Scrum can help your team stay organized and successful.
Managing Technical Debt in Agile Development

In Agile software development, technical debt is an important concept that helps teams balance speed and long-term sustainability. Agile focuses on delivering working software quickly, but technical debt highlights the costs of taking shortcuts during the development process. Let’s explore what technical debt means, its causes, impacts, and how to manage it effectively. What is Technical Debt? Technical debt refers to the extra work created when developers choose faster, less optimal solutions to meet immediate needs. Like financial debt, it grows over time, requiring more effort and resources to fix. Ignoring it can lead to bigger problems later. Types of Technical Debt There are several types of technical debt, including: Causes of Technical Debt in Agile Many factors contribute to technical debt in Agile projects. The focus on delivering software quickly can lead to rushed decisions. Changing requirements can force teams to rework code, introducing inconsistencies. Skipping thorough code reviews, neglecting documentation, and having poor testing processes can all add to the debt. Impacts of Technical Debt If left unchecked, technical debt can slow down projects and harm team productivity. Developers may spend more time fixing issues instead of building new features. This increases costs and can lead to bugs or poor performance. Over time, frustration with messy code can lower team morale. Managing Technical Debt in Agile To keep technical debt under control, teams can take a few key steps: Balancing Innovation and Maintenance Technical debt isn’t always bad—it can be a useful tool for meeting deadlines. However, managing it effectively ensures it doesn’t grow out of control. By addressing technical debt as part of the Agile process, teams can deliver innovative solutions without compromising on long-term success. In summary, technical debt is a normal part of software development. When teams understand its causes and plan for it, they can balance speed and sustainability, ensuring their projects stay efficient and their code stays manageable.
Agile Failures: What Goes Wrong and How to Fix It

Agile is known for improving teamwork, speeding up delivery, and helping organizations adapt to change. However, not every Agile transformation succeeds. Many real-life failures offer important lessons about what went wrong and how to fix it. Misunderstanding Agile Principles One common issue is adopting Agile practices, like daily stand-ups or sprints, without understanding their purpose. Teams often follow these rituals mechanically without truly embracing agility. This is sometimes called “Zombie Agile.” How to Fix It:Teach teams and leaders about the Agile Manifesto and its principles. Agile is about delivering value, responding to change, and working closely with customers. Adapt the framework to fit your team’s needs instead of treating it as a strict set of rules. Top-Down Agile Implementations Agile often fails when leaders force it on teams without their input. Processes and tools are imposed, leading to frustration and resistance. How to Fix It:Include teams in the decision-making process. Let them take ownership of Agile practices and create space for open feedback. Leaders should guide and support, not micromanage. Collaboration and transparency are essential for Agile to work. Lack of a Cultural Shift Agile can’t thrive in a culture based on rigid hierarchies, micromanagement, or a fear of failure. If the organization’s culture doesn’t support trust and collaboration, Agile practices won’t succeed. How to Fix It:Build a culture that matches Agile values. Encourage open communication, learning from mistakes, and teamwork. Leaders should lead by example by being transparent, adaptable, and collaborative. Ignoring Technical Excellence Sometimes teams focus so much on delivering quickly that they ignore technical quality. This can lead to poorly built systems, frequent bugs, and growing technical debt. How to Fix It:Make technical excellence a priority. Use tools and methods like automated testing, continuous integration, and pair programming. Agile isn’t just about speed—it’s also about creating sustainable, high-quality work. Overloading Teams Organizations sometimes see Agile as a way to push teams to do more in less time. Unrealistic goals, too many meetings, and constant task-switching can overwhelm teams and lead to burnout. How to Fix It:Respect the team’s capacity and focus on delivering fewer, more valuable items. Measure progress through healthy team practices, not just output. A balanced workload keeps teams productive and motivated. Failing to Measure Success Without clear metrics, it’s hard to tell if Agile is working. This can cause teams to lose focus and stakeholders to lose confidence. How to Fix It:Define success with clear goals, like faster delivery times, better customer feedback, or increased ROI. Track these metrics regularly to identify what’s working and where to improve. Not Adapting to Change Ironically, some Agile teams struggle to adapt. They stick rigidly to their plans even when customer needs or market conditions change. How to Fix It:Encourage teams to re-evaluate and adjust their plans regularly. Product owners should actively gather feedback and update priorities. Flexibility is a key part of Agile—use it to respond effectively to change. Conclusion Agile often fails because teams lose sight of its core principles. Focusing too much on processes and tools, without addressing teamwork and adaptability, leads to problems. However, every failure offers a chance to learn and improve. Agile isn’t a quick fix—it’s a mindset. With the right approach, even setbacks can pave the way for success.
Challenges Faced by Scrum Masters and How to Tackle Them

A Scrum Master has a big job guiding teams through Agile methods, keeping them productive, and making sure they follow Scrum rules. Even experienced Scrum Masters face challenges, but here are some common ones and ways to handle them. 1. Managing Stakeholder Expectations Scrum Masters often struggle with balancing what stakeholders want and what the team can realistically deliver. Stakeholders may push for quick results or extra features, which can overwhelm the team and lead to burnout. Solution: Open communication is key. Scrum Masters should keep stakeholders informed about the team’s capacity and show how adding extra work impacts deadlines. Using charts or data like team velocity can help stakeholders see what’s realistic. Educating stakeholders on Agile values, such as working at a sustainable pace, can also make a big difference. 2. Dealing with Resistance to Change Teams used to traditional project management may resist Agile methods, feeling uncomfortable with new roles or frequent check-ins. This can lead to skipped meetings or doubts about the Agile approach. Solution: Scrum Masters should be patient, acting as coaches. Hold workshops to explain Agile basics and show how Scrum benefits the team, such as by enabling quick feedback. Encourage the team to try new things and adapt slowly, celebrating small successes along the way to build trust in the process. 3. Ensuring Team Collaboration Sometimes team members don’t collaborate well, especially in remote teams. Miscommunication, delays, and working in silos can slow down the process. Solution: Scrum Masters can promote teamwork by organizing team-building activities and setting up clear channels for communication. Daily stand-ups and regular retrospectives help team members share updates and voice issues. For remote teams, use tools that support collaboration and establish communication guidelines. Building a supportive environment where everyone feels comfortable sharing can also boost collaboration. 4. Managing Scope Creep In Agile, flexibility can sometimes lead to “scope creep,” where extra features are added continuously. This often happens when priorities aren’t clear, putting pressure on the team. Solution: Scrum Masters should work closely with the Product Owner to keep the backlog organized and prioritize tasks based on value. Remind the team of the sprint goal and help them commit only to tasks they can complete in the sprint. For new requests, explain their impact on current work and suggest adding them to future sprints. 5. Handling Conflicting Personalities Teams are diverse, with members bringing different perspectives and working styles. Conflicts can arise, affecting teamwork and productivity. Solution: Scrum Masters should promote respect and open communication. Encourage team members to express their ideas and address conflicts openly. Private coaching sessions may also help. Setting team rules and modeling respectful behavior can guide the team toward healthier collaboration. 6. Promoting Continuous Improvement Teams can become comfortable and stop seeking improvements, which can reduce productivity over time. Solution: Scrum Masters should make retrospectives a safe, engaging space for feedback. Try different retrospective formats to keep them fresh and encourage honest reflection. Set improvement goals and check in on them in the next sprint. Supporting continuous learning and adapting based on feedback can keep the team motivated and productive. Conclusion Being a Scrum Master has challenges, from managing expectations to encouraging teamwork. But with clear communication, patience, and dedication to Agile principles, these challenges can become growth opportunities. Overcoming these obstacles helps the team work better together, adapt to change, and deliver quality results, making Agile truly effective.
Essential Skills Every Scrum Master Needs

A Scrum Master plays a key role in helping teams work well within Agile practices, especially when using Scrum. They’re not just in charge of meetings but support the whole team and organization to follow Agile principles effectively. Here are the main skills a good Scrum Master needs. 1. Facilitation and Communication Skills A Scrum Master runs meetings like sprint planning, daily stand-ups, sprint reviews, and retrospectives. They make sure these meetings are focused, organized, and productive. This means they need to guide discussions and encourage everyone to participate. Communication is essential because the Scrum Master acts as a bridge between the development team, the Product Owner, and other stakeholders. They should explain things clearly, avoid jargon, and ensure everyone is working toward the same goals. 2. Coaching and Mentoring A big part of the Scrum Master’s job is to coach and support the team. They help team members understand and use Agile principles, encouraging them to take charge of their work. Rather than giving answers directly, they guide the team with questions, helping them find solutions themselves. This approach builds a culture of learning and growth, which is important for Agile teams. 3. Conflict Resolution and Negotiation Conflicts happen in any team, and a Scrum Master should know how to resolve them positively. Whether it’s disagreements over priorities, resources, or personal differences, they need to manage conflicts calmly and fairly. This involves listening actively, showing patience, and having a problem-solving attitude. Scrum Masters also act as neutral helpers, allowing team members to express their concerns and work toward a solution together, keeping the team unified. 4. Servant Leadership Being a Scrum Master is about servant leadership—empowering the team rather than managing or controlling them. They focus on supporting the team by removing roadblocks and helping them work smoothly. A servant leader puts the team’s needs first, builds trust, and creates a safe environment. They protect the team from distractions so they can stay focused on delivering results for the customer. 5. Knowledge of Agile and Scrum While people skills are crucial, a Scrum Master also needs a solid understanding of Agile principles and the Scrum framework. They should know what each part of Scrum is for, like the product backlog, sprint backlog, and increment, and how to manage these effectively. They should be comfortable using tools like story mapping and tracking velocity to help the team make decisions. They should also adjust these practices to fit the unique needs of the team and organization. 6. Adaptability and a Focus on Improvement Adaptability is key in Agile environments. A good Scrum Master is open to change and always looking for ways to improve. They should keep learning, stay updated on new Agile ideas, and refine their own approach. By being adaptable and showing a commitment to improvement, they encourage the team to stay flexible and improve over time. In short, a Scrum Master needs a blend of skills: good communication, conflict resolution, a deep understanding of Agile and Scrum, and a focus on serving the team. By mastering these skills, Scrum Masters can help the team work together effectively, deliver quality results, and create real value for the organization and its customers.
8 Simple Ways to Make Your Daily Scrum Fun and Engaging

Daily Scrums can sometimes feel repetitive and lose their energy, making it hard for team members to stay engaged. But with a few changes, you can make these meetings something people look forward to. Here’s how to add some fun, variety, and value to your Daily Scrum: 1. Switch Up the Setting and Style If you’re always meeting in the same spot, try switching it up! Change locations, try a virtual background, or even go outside. For a fresh twist, do a “walking stand-up” where everyone moves around as they talk. Changing the environment or style brings new energy and keeps things from feeling stale. 2. Rotate the Leader Having the same person (often the Scrum Master) lead each time can get repetitive. Let team members take turns leading the Scrum. This keeps things fresh and gives everyone a sense of ownership. Plus, different leaders bring different styles and ideas, making each meeting unique. 3. Add Themes or Daily Focuses Make each day special by giving it a theme or focus. For example, Mondays could be “Problem-Solving Day,” where team members share any obstacles they’re facing. Tuesdays could be “Takeaway Day,” where each person shares a lesson learned. These small changes can help the team look forward to each day’s Scrum with new purpose. 4. Share Small Personal Updates Start each meeting with a quick personal update or a positive note from each person. A quick check-in or “what’s one small win you’ve had recently?” helps team members connect on a personal level. This brings a human touch to the meeting and strengthens team bonds. 5. Use Visuals and Stories Try using visual tools like Kanban boards, project timelines, or virtual boards to make updates more engaging. Team members can walk the group through visuals to show progress. Even better, have them frame their updates like a mini-story, starting with what they tackled yesterday and what they’re taking on today. This keeps the meeting engaging and clear. 6. Set Time Limits and Gamify To keep the meeting moving, set a timer for each person’s update. This encourages everyone to keep it brief and focused. You could also gamify it: award points when the meeting finishes on time, and celebrate with a team reward when you reach a set goal. 7. Focus on Problems, Not Just Status If the Scrum is just a checklist of what everyone did, people can lose interest. Encourage team members to share any blockers they’re facing, and have the group brainstorm quick ideas to help. If a longer discussion is needed, decide who will meet later to solve it. This keeps the Scrum focused on solving real issues rather than just giving updates. 8. Celebrate Wins and Boost Team Morale Wrap up the meeting by celebrating small wins. This can be as simple as giving kudos to someone who overcame a challenge or reached a milestone. Small celebrations create a positive atmosphere and keep everyone motivated. These simple changes can make your Daily Scrums more enjoyable, focused, and valuable. By keeping things fresh and centered on collaboration, you’ll help your team look forward to each day’s work with renewed energy.
How to Make Daily Scrum Meetings More Interesting

Daily Scrum meetings are essential in Agile project management, helping teams stay on the same page, share updates, and adjust plans when needed. However, these meetings can sometimes become boring or feel repetitive. When this happens, people might lose focus, and the meeting may not provide as much value. So, how can we make daily Scrums more engaging and enjoyable? Here are some simple tips to keep your daily Scrum meetings interesting and productive: 1. Keep It Short and Focused A daily Scrum should be quick and to the point—no more than 15 minutes. If it regularly takes longer, it’s likely losing the team’s attention. Stick to the core questions:What did you do yesterday? What will you do today? Do you have any blockers? Encourage brief updates and avoid lengthy discussions. Keeping the meeting short and focused ensures it remains energizing, not tiring. 2. Mix Up the Meeting Format Doing the same thing every day can get boring. Try changing how you run the meeting now and then. Changing the routine makes the meeting less predictable and keeps the team engaged. 3. Use Visual Tools Using visuals during Scrum can make the meeting more dynamic. If you’re working with digital tools like Jira, Trello, or Asana, display them on a screen and walk through the tasks. Visual aids help clarify what’s being discussed and keep everyone interested. For virtual teams, try using fun virtual backgrounds or team avatars to create a more interactive experience. 4. Celebrate Small Wins While Scrum is mostly about tracking progress and solving problems, don’t forget to celebrate achievements, no matter how small. Whether it’s finishing a task or overcoming a challenge, take a moment to recognize these wins. A simple acknowledgment or quick round of applause can lift the team’s spirits and make the meeting more enjoyable. 5. Rotate the Scrum Master Role Let different team members take turns leading the Scrum. This brings fresh perspectives and energy to the meeting. Each person might have a different style of running the meeting, which keeps things from getting stale. It also promotes a sense of shared responsibility within the team. 6. Tackle Blockers Effectively Blockers (things stopping progress) are a key part of Scrum. However, if the same blockers come up day after day without any resolution, it can frustrate the team. Make sure blockers are addressed quickly, either in the meeting or right after. This shows the team that the Scrum is a useful tool for solving problems, not just a daily task to check off. 7. Add Some Fun A little fun can go a long way in making Scrum more enjoyable. Here are some simple ideas: 8. Encourage Team Interaction Scrum shouldn’t just be about giving updates to the Scrum master. Encourage team members to talk to each other, offer help, or brainstorm ideas together during the meeting. This makes the Scrum more about teamwork and collaboration, rather than just individual status reports. Conclusion Making daily Scrum meetings interesting doesn’t require big changes. By keeping them short, using visuals, rotating roles, and adding a bit of fun, you can create a meeting that your team looks forward to. Scrum is meant to be valuable and productive, and with these small adjustments, you can make sure it benefits everyone involved.
How to Create the Perfect Scrum Board for Agile Teams
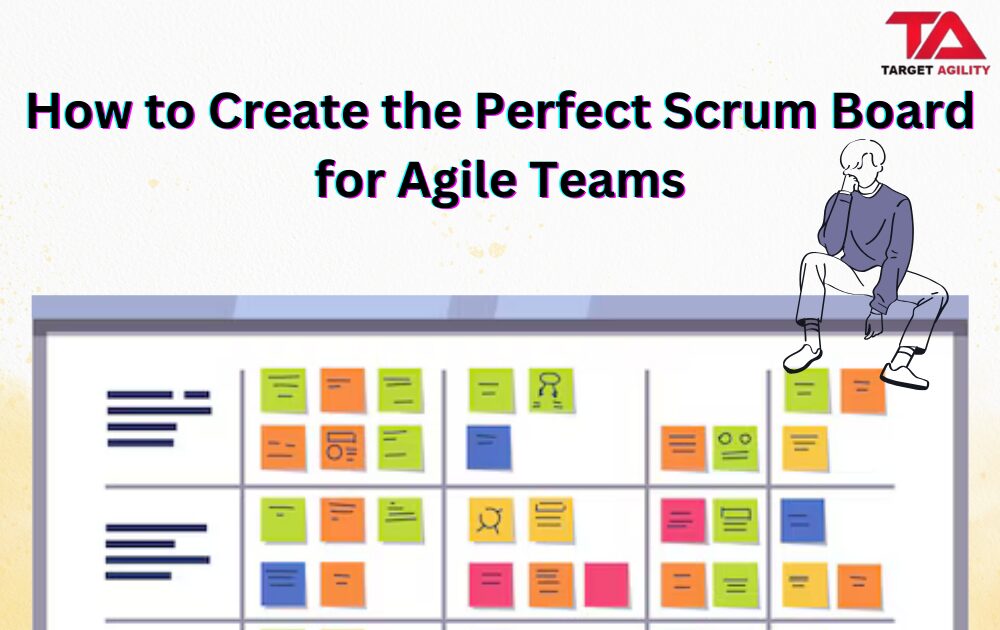
A Scrum board is a simple yet powerful tool that helps Agile teams stay organized and keep track of their work. It visually shows the progress of tasks, helping everyone stay on the same page. Whether you prefer a physical board or a digital one, setting up a Scrum board correctly can make managing tasks easier and improve team efficiency. Here’s how you can create a great Scrum board for your team. 1. Get to Know the Basic Structure of a Scrum Board A Scrum board usually has columns that represent the different stages of work. These columns typically include: You can customize these columns to fit your team’s process. For example, if you often have tasks that get blocked, you can add a “Blocked” column. The goal is to clearly show where each task is in the workflow, from start to finish. 2. Use Cards to Represent Tasks Each task or user story on the Scrum board is represented by a card. The card should include key details like: In digital Scrum boards, you can add more features like comments, labels, or attachments to provide more context for each task. 3. Set Limits for Work in Progress (WIP) To avoid overwhelming your team with too many tasks at once, set Work In Progress (WIP) limits. This means you limit how many tasks can be in certain columns, especially “In Progress,” at one time. This helps the team focus on finishing tasks before starting new ones, reducing distractions and bottlenecks. 4. Promote Transparency and Team Collaboration Your Scrum board should make it easy for everyone to understand the current state of tasks. Each team member should be able to see what’s being worked on and who’s responsible for what. This promotes transparency and encourages better teamwork. 5. Track Progress and Improve Over Time As your team works, gather data from the Scrum board to track progress and spot areas for improvement. You can track: By analyzing this data, you can identify ways to improve your team’s workflow. For example, if tasks are often delayed in the “In Progress” column, you might consider breaking them down into smaller steps or adjusting your WIP limits. Conclusion A well-organized Scrum board is a key tool for keeping your Agile team on track. By setting up clear columns, using detailed task cards, limiting work in progress, and promoting transparency, your Scrum board will help your team work more efficiently. Whether it’s a physical board or a digital tool, maintaining it well will ensure your team can easily manage tasks and achieve their sprint goals.
How to Connect Scrum Developers with Customers: Easy Ways to Improve Teamwork

In software development, maintaining a strong connection between the development team and the customers is crucial to ensure the product meets user needs and receives timely feedback. Scrum, a popular project management framework, emphasizes the importance of this connection, but keeping it strong can be challenging. Here are some practical ways to enhance collaboration between developers and customers in Scrum. 1. Involve Developers in Sprint Reviews A Sprint Review takes place at the end of each Sprint (typically 1-4 weeks) where the team showcases their completed work. While the Product Owner usually leads the meeting, it’s beneficial to have developers actively participate. When developers present their work directly to customers, they can: This direct engagement helps developers see the real-world impact of their work and make timely adjustments based on customer insights. 2. Invite Customers to Planning Sessions In Scrum, regular planning meetings help organize the team’s work. Involving customers in these sessions can be valuable as developers gain direct input from the people who will be using the product. By asking questions and clarifying requirements during planning, developers can avoid misunderstandings and ensure they’re working on the features that matter most to customers. 3. Encourage Regular Customer Feedback Consistent feedback from customers is vital for keeping the project aligned with their expectations. Some effective ways to gather feedback include: By receiving feedback firsthand, developers can make improvements more quickly and effectively. 4. Use Customer Personas and Journey Maps Customer personas and user journeys are helpful tools for keeping the team focused on customer needs: These tools guide developers in creating features that address real customer problems and enhance the overall user experience. 5. Enable Direct Communication Between Developers and Customers Although the Product Owner typically communicates with customers, there are times when developers need to clarify technical details. Establishing quick communication channels, such as short meetings or messaging systems, allows developers to get answers directly and quickly, reducing delays and misunderstandings. 6. Facilitate Connections Through the Product Owner The Product Owner serves as the main link between the development team and the customers. While they guide the project, they can also help facilitate direct communication when necessary, such as setting up quick discussions for resolving specific customer concerns. By promoting these direct interactions, the Product Owner ensures the team remains aligned with customer needs. 7. Incorporate Customer Feedback into Team Discussions During the Sprint Retrospective, where the team reflects on what went well and what can be improved, discussing customer feedback can be highly valuable. This keeps the team focused on delivering a product that meets user needs. Key questions might include: This process encourages continuous improvement and ensures that customer feedback remains a central part of the team’s work. Conclusion Fostering a strong connection between developers and customers is essential for building a product that truly addresses user needs. By involving developers in key meetings, encouraging direct communication, and gathering regular feedback, teams can enhance collaboration and deliver more valuable products. When developers and customers work closely, the team can respond more quickly to customer needs, resulting in a product that offers real value.
Why Choose ICAgile: A Simple Guide to Elevating Your Agile Skills

In today’s fast-changing world, businesses are constantly seeking ways to improve and adapt. Agile methodologies have become a go-to choice for companies looking to manage projects more effectively, enhance teamwork, and deliver value faster. Among the many Agile certification options, ICAgile (International Consortium for Agile) stands out for its learner-focused and flexible approach. Here are some key reasons why ICAgile is a great choice for advancing your Agile skills and mindset. 1. Focus on Practical Learning ICAgile takes a different approach to learning compared to many other certification programs. Instead of focusing on exams and memorizing facts, ICAgile emphasizes real-world experience and deep understanding. The goal is to help people truly learn by doing, not just studying. The courses encourage hands-on practice and reflection, helping learners develop skills they can apply to actual projects. This makes ICAgile certifications more than just a piece of paper; they represent real knowledge and a genuine Agile mindset. 2. Variety of Learning Paths ICAgile offers a wide range of learning tracks tailored to different roles and needs within the Agile world. Whether you’re a project manager, a business analyst, a developer, or a leader, ICAgile has a course designed just for you. The two main paths are: Within these paths, you can choose from specializations like Agile Coaching, Team Facilitation, or Leadership. ICAgile certifications are structured to allow you to advance from beginner to expert as you grow, giving you a clear way to improve your skills over time. 3. Globally Recognized ICAgile certifications are respected worldwide. As Agile becomes more popular across industries, having a globally recognized certification can help you stand out in your career. ICAgile-certified professionals are known for not just understanding Agile principles but also for applying them effectively in their work. With training partners around the globe, ICAgile certifications are valued in many regions and industries, from tech to marketing and even HR. 4. Staying True to Agile Values ICAgile’s training programs focus on the core values and principles of the Agile Manifesto. This means that the certification is not just about using tools or following processes; it’s about understanding the human side of Agile, such as teamwork, flexibility, and delivering value. By choosing ICAgile, you’re aligning with an organization that values collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement. It’s not just about “doing Agile” but about “being Agile” in your mindset and approach. 5. Flexible Training Options ICAgile is known for its flexibility. Instead of having one fixed curriculum, it sets learning objectives and allows its accredited partners to create courses that meet those goals. This means you can find training that suits your industry or personal preferences. Additionally, ICAgile certifications don’t expire. Unlike other certifications that require you to retake exams or pay renewal fees, ICAgile certifications last a lifetime. This approach supports continuous learning, allowing you to focus on growing your skills instead of worrying about renewals. 6. Commitment to Continuous Improvement One of the key ideas behind ICAgile is continuous learning and improvement. Their courses encourage learners to reflect on their experiences, learn from them, and make changes as needed. This focus on growth ensures that Agile professionals can adapt to changes in their business environment and keep improving their skills. This mindset is ideal for Agile professionals who want to not only improve their processes but also drive innovation in their organizations. ICAgile helps Agile practitioners stay ahead of trends and best practices by fostering a culture of learning and improvement. Conclusion ICAgile offers a flexible, practical, and values-driven approach to Agile certification. Whether you’re just starting out or you’re already an experienced Agile practitioner, ICAgile provides a pathway to deepen your skills and adopt a lasting Agile mindset. By choosing ICAgile, you’re not just earning a certification—you’re gaining real-world knowledge and tools that will benefit both your career and your organization. “Click here to Join our ICAgile-certified course to master Agile skills and boost your career!”
Why Scrum Masters Are More Important Than Ever

As businesses adapt to fast changes in technology and market needs, many have turned to Agile methods to manage projects and deliver results quickly. Among the different Agile frameworks, Scrum is one of the most widely used. A key player in the Scrum process is the Scrum Master—a person responsible for helping teams work efficiently and follow Scrum practices. But with the constant changes in the workplace, one might wonder: Are Scrum Masters still in demand? The short answer is yes. Let’s take a look at why Scrum Masters continue to be important and how their role has changed over time. The Importance of Agile Agile methodologies, like Scrum, Kanban, and Lean, have become essential for delivering projects efficiently. They allow teams to work in short cycles, adapt to changes, and deliver value to customers faster. As more companies adopt Agile to stay competitive, the need for Scrum Masters grows. Scrum Masters help teams understand and follow the principles of Agile, encouraging collaboration, flexibility, and continuous improvement. What Does a Scrum Master Do? Many people think that Scrum Masters are project managers who assign tasks, but their role is actually quite different. A Scrum Master acts as a servant-leader, meaning their job is to support the team and help them succeed. Some key responsibilities include: These responsibilities highlight why Scrum Masters are so important—they help teams communicate better, collaborate efficiently, and improve their workflows, which are crucial in today’s fast-paced business world. Demand Across Different Industries While Scrum began in software development, its principles are now being used in a variety of industries, such as marketing, healthcare, finance, and more. As these industries adopt Agile, the demand for Scrum Masters has expanded beyond tech companies. Businesses in areas like manufacturing, logistics, and even government agencies are turning to Agile frameworks like Scrum to increase efficiency and deliver better results. For example, in industries like healthcare or finance, where there are strict regulations and fast-changing requirements, Agile helps teams meet goals more quickly. Scrum Masters in these sectors help teams navigate complex rules while maintaining flexibility and delivering high-quality results. How the Scrum Master Role Has Evolved As more companies adopt Agile, the role of the Scrum Master has also changed. Today’s Scrum Masters need to know more than just the basics of Scrum. In larger organizations, they may need to be familiar with scaling Agile frameworks, like Scrum@Scale, SAFe, or LeSS, which are used to manage larger teams or multiple projects at once. Additionally, the shift to remote work has changed how Scrum Masters operate. Virtual teams come with new challenges, such as ensuring effective communication across different time zones. Scrum Masters now play a key role in keeping remote teams connected and ensuring they collaborate smoothly, even when they are not in the same location. Why Scrum Masters Are Valuable Because of the wide range of tasks they handle, Scrum Masters bring significant value to organizations. They help reduce the time it takes to get products to market, improve the quality of work, and foster better teamwork. These benefits have kept Scrum Masters in demand across industries. Platforms like LinkedIn and Glassdoor consistently rank Scrum Master as a top job, especially in tech and project management fields. Conclusion: Are Scrum Masters Still Needed? Absolutely. Scrum Masters are still in high demand, and their role is becoming even more important. As more companies embrace Agile methodologies, both in technical and non-technical areas, the need for skilled Scrum Masters continues to grow. In addition, the challenges of remote work and managing larger teams make their role even more essential. If you’re thinking about becoming a Scrum Master or already working as one, you can feel confident that your skills will remain valuable for many years to come. “Ready to take your career to the next level? Join our Scrum Master course today and make it happen! Click here to get started!”
What Is a Release Train Engineer: Roles, Responsibilities, & Skills

A Release Train Engineer (RTE) plays a key role in Agile frameworks, particularly in the Scaled Agile Framework (SAFe). The RTE is like the head Scrum Master, overseeing a group of teams called the Agile Release Train (ART), which work together to deliver value consistently. The RTE’s job is to ensure that everything runs smoothly, teams stay aligned, and they meet the organization’s goals. In this blog, we’ll break down the RTE’s roles, responsibilities, and the skills they need. What Does a Release Train Engineer Do? The main job of an RTE is to make sure the Agile Release Train (ART) runs effectively. This involves helping teams stay in sync, solving issues, managing risks, and promoting collaboration. Here are some important tasks RTEs handle: Responsibilities of a Release Train Engineer An RTE’s responsibilities cover both the day-to-day operations of the Agile Release Train and the overall success of the program. Key responsibilities include: Skills Needed for a Release Train Engineer An effective Release Train Engineer needs a combination of technical knowledge, leadership, and communication skills. Some of the essential skills include: Conclusion The Release Train Engineer is essential to the success of the Agile Release Train in a SAFe setup. They ensure teams are aligned, risks are managed, and value is consistently delivered. Understanding the RTE’s roles, responsibilities, and necessary skills helps organizations run more efficient Agile processes and continuously improve their work. “Ready to kickstart your RTE journey? Click here to begin your adventure!”
What Does a Product Owner Do, and Why Are They Important?

In software development, the Product Owner (PO) is a key person who helps make sure the team works on the right things to bring value to the business. The role is important in Agile methods, especially in a process called Scrum. But what exactly does a Product Owner do? When do they do these tasks, and why are they so important? What Does a Product Owner Do? A Product Owner acts as a link between the business and the development team. Their job is to make sure the team focuses on the tasks that matter most. They gather information from stakeholders (people with an interest in the project), prioritize tasks, and decide what will give the most value to the product. In Scrum, the Product Owner manages a list of things the team needs to do, called the product backlog. This backlog includes features, updates, and fixes that the team will work on in future sprints (short work cycles). Key Responsibilities of a Product Owner Why Is the Product Owner So Important? Conclusion The Product Owner plays a crucial role in helping the development team deliver the right features to meet business goals and customer needs. They define the product vision, manage the product backlog, write user stories, and make real-time decisions to keep the project moving. Acting as a bridge between stakeholders and the development team, the Product Owner ensures that the team focuses on the most valuable work, making their role vital for the success of any Agile project.
Agile vs DevOps

When it comes to creating and delivering software, two popular methods are Agile and DevOps. Both help teams work better and faster, but they do it in different ways. Let’s break down what each one is and how they are different. What is Agile? Agile is a way of working that focuses on being flexible and working together as a team. Instead of trying to build the entire product all at once, Agile teams work in small steps, called sprints, which usually last 1 to 4 weeks. At the end of each sprint, they deliver a small, working part of the product. Agile also involves getting feedback from customers regularly so the team can make improvements as they go. The main idea is to make changes quickly based on what users need. The key values of Agile are: In short, Agile is all about working in small steps, delivering pieces of the product often, and being open to change. What is DevOps? DevOps is a way of working that helps teams build, test, and release software faster and more reliably. It focuses on improving the communication between two groups: the development team (the people who build the software) and the operations team (the people who manage and support the software after it’s built). The main goals of DevOps are: DevOps is about making sure the whole process— from writing code to keeping it running— is smooth and fast. How are Agile and DevOps Different? 1. What They Focus On 2. Who’s Involved 3. Work Process 4. Use of Automation 5. Getting Feedback 6. Company Culture Can Agile and DevOps Work Together? Yes! In fact, they often go hand in hand. Agile helps teams develop software quickly, while DevOps ensures that the software is released and maintained properly. For example, a team might use Agile to manage how they build software and use DevOps to manage how that software is tested, deployed, and run in real life. Together, Agile and DevOps can help teams create software faster and more reliably. Conclusion Agile and DevOps both aim to improve how software is developed and delivered, but they do it in different ways. Agile focuses on the development team, working in short cycles and delivering small updates. DevOps focuses on the whole process, from development to deployment, using automation and better teamwork between developers and operations. When combined, Agile and DevOps can help teams deliver better software faster and more efficiently.
Scrum Master vs. Project Manager: What’s the Difference?
When it comes to managing projects, two roles often come up: Scrum Master and Project Manager. Both are important, but they work in different ways and have different responsibilities. Understanding what sets them apart can help you decide which one is the right fit for your project or organization. What Does a Scrum Master Do? A Scrum Master works within Agile frameworks, specifically the Scrum methodology. Agile is all about being flexible and working in small, manageable steps. The Scrum Master’s main job is to guide the team, making sure everyone is following the Scrum process and staying productive. Key Responsibilities: A Scrum Master doesn’t make decisions about the project’s budget, timeline, or scope. Instead, they focus on making sure the team works well within the Agile framework. What Does a Project Manager Do? A Project Manager is often found in more traditional project management methods like Waterfall, where projects follow a strict sequence. The Project Manager is responsible for the entire project, managing both the team and outside stakeholders. Key Responsibilities: Unlike Scrum Masters, Project Managers handle everything from start to finish, including making key decisions about timelines, resources, and the overall direction of the project. Main Differences Conclusion: Which Role is Better? Neither role is better than the other; it really depends on the type of project and how the company likes to work. A Scrum Master might be better for Agile projects that need flexibility and teamwork. On the other hand, a Project Manager might be a better fit for long-term projects that require detailed planning and strict deadlines. Both roles are valuable in their own ways, and the best choice depends on the project’s needs and goals.
Boost Your Scrum Performance: An Easy Guide for Agile Teams

Scrum is a popular method used to manage projects, especially in software development. It helps teams work together efficiently and deliver high-quality products faster. However, even though Scrum is straightforward, it takes practice and effort to get really good at it. In this guide, we’ll share simple tips to help you and your team improve your Scrum performance. 1. Learn the Basics Well To do well in Scrum, everyone on the team needs to understand how it works. This means knowing the three main roles (Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team), the five key meetings (like Sprint Planning and Daily Stand-up), and the three important documents (Product Backlog, Sprint Backlog, and Increment). Tip: Make sure everyone on the team knows their role and responsibilities. Consider reading the Scrum Guide or attending a Scrum workshop to refresh your knowledge. 2. Set Clear and Achievable Goals One common problem in Scrum is unclear or unrealistic goals. During Sprint Planning, the Product Owner and the team should work together to create specific, doable goals for each sprint. These goals should fit within the sprint time and match the overall project vision. Tip: Use user stories or other tools to break down tasks clearly. This helps everyone know what they’re working toward and stay focused. 3. Improve Sprint Planning and Backlog Organization Good Sprint Planning is key to a successful sprint. This means making sure the Product Backlog is organized and that only the most important tasks are included in the Sprint Backlog. Regular backlog grooming helps keep things clear and prioritized. Tip: Have regular meetings to review and clean up the backlog. This makes planning sprints easier and more effective. 4. Encourage Communication and Teamwork Scrum works best when the team communicates well. The Daily Stand-up is one way to ensure everyone stays on the same page, but team members should communicate openly throughout the sprint, not just in meetings. Tip: Create an environment where team members feel comfortable speaking up about challenges or ideas. Use tools like Slack or Microsoft Teams to stay connected, especially if your team works remotely. 5. Make the Most of Retrospectives The Sprint Retrospective is a valuable meeting where the team reviews what went well and what needs improvement. It’s a chance to find ways to get better each sprint. Tip: Make sure retrospectives are open, honest, and focus on taking actions to improve. Then, apply those lessons in the next sprint to keep getting better. 6. Keep Daily Stand-ups Short and Focused The Daily Stand-up is a quick meeting designed to help the team stay aligned. However, it can easily become too long or off-topic if not managed well. Tip: Stick to the basics: What did you do yesterday? What are you working on today? Do you have any blockers? This keeps the meeting short and effective. 7. Support the Scrum Master The Scrum Master plays a key role in making sure the team follows Scrum rules and improves over time. They help remove obstacles and make sure the team can work smoothly. Tip: Give the Scrum Master the support they need to solve problems and keep the team focused. A strong Scrum Master helps the team perform at its best. 8. Track Progress with Metrics To improve, it’s important to measure how the team is doing. Metrics like sprint velocity, burndown charts, and cycle time can show whether the team is improving or facing problems. Tip: Regularly review these metrics during Sprint Reviews or Retrospectives. Use them to start conversations about how the team can get better. 9. Encourage Responsibility and Ownership Scrum teams work best when everyone takes responsibility for their work. When team members feel accountable, they are more motivated and engaged in achieving the sprint goals. Tip: Encourage a culture where team members take ownership of their tasks. This builds trust and makes the team stronger. 10. Stay Flexible and Adaptable Scrum is designed to be flexible. Be ready to adapt and make changes when necessary, especially as the project or client needs evolve. Scrum’s iterative process allows teams to adjust as they go. Tip: Don’t be afraid to make changes during the project. Staying flexible helps the team respond to new challenges and deliver better results. Conclusion Improving Scrum performance takes continuous effort, but by focusing on understanding the framework, setting clear goals, improving communication, and being open to change, your team can deliver better results more efficiently. Scrum is all about collaboration, adaptability, and continuous improvement, so encourage your team to embrace these values.
Striking the Right Balance for Documentation in Agile Projects

In Agile projects, determining the right amount of documentation can be a challenge. While traditional project management methods rely on extensive paperwork, Agile emphasizes working software over comprehensive documentation. Despite this, some level of documentation remains crucial to maintain clarity and organization. The key is finding the right balance—providing enough documentation to support the team without slowing progress. 1. Understand the Purpose of Documentation Before deciding how much documentation is needed, it’s important to clarify its purpose. In Agile, documentation should serve a specific function, adding value to the project. The primary purposes of documentation are to share critical information with stakeholders and new team members, explain complex features or processes, and keep a record of important decisions for future reference. Identifying these needs helps determine which documents are essential for the project. 2. Keep Documentation Simple and Useful Agile encourages keeping documentation minimal. Instead of creating lengthy, detailed documents, the focus should be on producing short, clear ones that directly support the team’s progress. Documents should provide only the necessary information to move forward without creating unnecessary workload. This helps the team stay agile and efficient while still maintaining clarity in communication. 3. Leverage Agile-Friendly Tools The right tools can help manage documentation more effectively. Agile teams often use digital platforms like Confluence, Jira, or Google Docs to create and update documents in real time. These platforms facilitate collaboration and ensure that documentation stays current as the project evolves. By using shared workspaces, the team can easily access and update documents, ensuring they remain relevant and useful throughout the project’s lifecycle. 4. Focus on What’s Necessary In Agile, the goal is to document just enough to support the team’s needs. Instead of creating long, detailed documents that may not be used, it’s important to focus on the most critical aspects of the project. These include high-level requirements, key design decisions, and project milestones. Short user stories can often replace detailed specifications, providing a clearer, more agile way to communicate features and goals. 5. Make Documentation Part of Your Workflow To keep documentation relevant and up to date, it should be integrated into the project’s regular workflow. Rather than treating documentation as a separate task to be completed later, teams should update it throughout the project. Regularly reviewing and maintaining documents during sprint planning or retrospectives ensures they reflect the current state of the project and align with its progress. 6. Collaborate on Documentation Documentation in Agile should be a team effort. Everyone on the team should contribute to creating and updating documents to ensure that they are accurate and complete. Collaboration among developers, testers, and the Product Owner ensures that documentation reflects diverse perspectives and captures all necessary information. This collaborative approach improves the quality and usefulness of documentation while preventing any single individual from shouldering the burden. Conclusion Balancing documentation in Agile projects requires providing just enough information to be useful without slowing down the team. By keeping documentation simple, relevant, and integrated into the regular workflow, Agile teams can maintain clarity, improve communication, and stay on track without sacrificing efficiency. Thoughtful documentation becomes a valuable tool that enhances project success, rather than a burden that holds the team back.
How AI is Changing DevOps: A Simple Guide

Artificial Intelligence (AI) is making big changes in many areas, including software development, where it’s transforming DevOps. DevOps combines development and operations to make software delivery and infrastructure management smoother. AI is helping DevOps teams by making processes smarter, predicting problems, and improving decision-making. Here’s a look at how AI is reshaping DevOps and the future of software development. 1. Boosting Automation Automation is a key part of DevOps, and AI makes it even better. While traditional automation tools follow set rules, AI can learn from data and adapt its actions. For example, AI can automate routine tasks like deploying code, setting up infrastructure, and configuring environments more accurately. By analyzing past data, AI can suggest the best setups and handle complex tasks that were once manual, reducing human error and increasing efficiency. 2. Predicting and Preventing Problems AI’s ability to predict and prevent issues is one of its biggest benefits in DevOps. AI can look at data from system logs, performance metrics, and user feedback to find patterns and spot potential problems before they happen. This allows teams to fix issues before they affect users, reducing downtime and making systems more reliable. 3. Smarter Monitoring and Analytics AI improves monitoring and analytics by giving deeper insights into how systems are performing. Traditional tools can generate a lot of data that’s hard to interpret. AI-powered tools can sift through this data, spot trends, and provide useful insights in real time. For example, AI can identify unusual behavior or performance drops that might be missed by traditional tools and suggest fixes. 4. Faster Incident Management AI helps manage incidents more effectively by quickly identifying and resolving issues. When a problem occurs, AI can analyze the data to find the root cause faster than manual methods. It can also automate the solution process, which speeds up resolution, reduces impact on users, and allows DevOps teams to focus on other important tasks. 5. Better Resource Management AI also improves resource management by optimizing how resources are allocated and scaled. It can analyze usage patterns and predict future needs, adjusting resources in real time based on current demands. This helps ensure that applications have the resources they need while avoiding excess costs and making cloud infrastructure more efficient. 6. Stronger Security Security is crucial in DevOps, and AI enhances it by spotting vulnerabilities and threats more effectively. AI security tools analyze network traffic, user behavior, and system access to detect suspicious activities. By constantly learning about new threats, AI provides better security measures and helps DevOps teams respond quickly to potential dangers. Conclusion AI is transforming DevOps by improving automation, predicting and preventing problems, enhancing monitoring, optimizing resources, and boosting security. As AI technology advances, it will continue to drive improvements in efficiency and performance in DevOps. By using AI, DevOps teams can streamline their work, reduce risks, and deliver software faster, leading to a more agile and effective development process. AI is a key player in the future of DevOps, making it smarter and more efficient.
The Surge in Scrum: Why Everyone Wants It
Scrum is taking the project management world by storm, and there’s a good reason for it. In this blog, we’ll explore why Scrum is in such high demand, what makes it tick, and how it’s changing the game for modern project teams. The Agile Shift To understand Scrum’s popularity, we need to look at the Agile revolution. Traditional project management methods struggled to keep up with the fast-paced business world. Then came Agile, a set of principles that prioritizes flexibility, teamwork, and customer satisfaction. Scrum, born out of Agile, became a top choice for organizations wanting to tackle the challenges of modern project delivery. Scrum Basics Scrum is a lightweight framework that offers a structured yet flexible approach to project management. It operates on the principles of transparency, inspection, and adaptation. Here are some key things that make Scrum special: The Scrum Boom Now, let’s look at why Scrum is so much in demand: Conclusion In summary, Scrum’s high demand in project management is because it effectively tackles the challenges of today’s fast-changing business environment. Its adaptability, teamwork, customer focus, and proven success stories make it a go-to framework for organizations striving to stay competitive. As the Agile movement continues to shape project management, Scrum stands out as a guide toward greater efficiency, customer satisfaction, and success. The journey of Scrum from a niche methodology to a global phenomenon reflects its enduring relevance and transformative impact on modern project management.
Scrum Framework: A Guide for New Team Members

In the fast-paced landscape of software development, staying agile and adaptable is crucial for success. Enter Scrum, a widely embraced framework that embodies these principles. For new team members, grasping the fundamental concepts of Scrum is essential. This blog post aims to unravel the core elements of Scrum, shedding light on how it encourages collaboration, transparency, and continuous improvement. Chapter 1: Scrum Basics At its heart, Scrum is an agile framework designed to boost the efficiency and effectiveness of teams tackling complex projects. It offers a structured yet flexible approach, emphasizing iterative and incremental development. The pillars of Scrum — transparency, inspection, and adaptation — form the bedrock of the framework. Chapter 2: Scrum Team Roles In the Scrum framework, three primary roles contribute to project success: the Product Owner, Scrum Master, and Development Team. Each role has distinct responsibilities, ensuring a well-balanced distribution of tasks and fostering collaboration. The Product Owner represents stakeholders, the Scrum Master facilitates the Scrum process, and the Development Team brings the product to life. Chapter 3: Scrum Tools Scrum utilizes several tools, or artifacts, to capture and communicate crucial information. The Product Backlog is a dynamic list prioritizing work to be done, while the Sprint Backlog is a subset chosen for a specific sprint. Burndown charts visually track work completed over time, providing insights into the team’s progress. Chapter 4: Scrum Events Scrum events are time-boxed ceremonies that structure the work of the Scrum Team. The Sprint is a fixed-length iteration where a potentially releasable product increment is created. Sprint Planning, Daily Stand-ups, Sprint Review, and Sprint Retrospective are key events ensuring team synchronization, transparency, and continuous improvement. Chapter 5: Sprint Planning Sprint Planning is a collaborative session where the team selects items from the Product Backlog for the upcoming Sprint. The Product Owner shares insights into high-priority items, and the Development Team collaborates on how to achieve the goals. By the end, the team commits to delivering a potentially shippable product increment by the Sprint’s conclusion. Chapter 6: Daily Stand-ups The Daily Stand-up is a brief, daily meeting where team members share progress, discuss impediments, and plan for the next 24 hours. This promotes communication, ensuring everyone is on the same page and fostering a sense of accountability and collective ownership. Chapter 7: Sprint Review At the Sprint’s end, the team conducts a Sprint Review to showcase completed work to stakeholders, inviting feedback. This ensures the product aligns with stakeholders’ expectations, and the Product Backlog is adjusted accordingly. Chapter 8: Sprint Retrospective The Sprint Retrospective is a dedicated time for the team to reflect on the previous Sprint, identifying successes and areas for improvement. It is a crucial step in the continuous improvement cycle of Scrum. Chapter 9: Scrum Values Scrum is not just about practices; it’s also grounded in five values: commitment, courage, focus, openness, and respect. These values guide the behavior of the Scrum Team, fostering a positive and collaborative working environment. Conclusion In summary, Scrum empowers teams to deliver value incrementally, adapt to changing requirements, and continuously improve. For new team members, embracing the principles, roles, artifacts, and events of Scrum is the first step toward unlocking its full potential. As they embark on their Scrum journey, a commitment to collaboration, transparency, and a mindset of continuous improvement will pave the way for successful and fulfilling projects.
Learning from Experience: The Key Principles in Scrum

Imagine a way of working that focuses on learning from experience to make things better. That’s what empiricism is all about, and it’s especially crucial in the world of Scrum, an approach used in project management. Let’s take a closer look at how the Three Pillars of Empiricism—Sensation, Reflection, and Experience/Experimentation—are the backbone of Scrum, helping teams be successful and adaptable. Pillar 1: Sensation in Scrum In Scrum, Sensation is like paying attention to what’s happening during the project. It’s all about gathering information as the team works. Daily Standups and Sprint Reviews are meetings where the team shares what’s going well and what challenges they’re facing. This constant sharing of information helps the team stay aware and make decisions based on what’s actually happening in real-time. Pillar 2: Reflection in Scrum Reflection in Scrum means thinking about what’s been happening and figuring out how to make things better. The Sprint Retrospective is a special meeting where the team looks back at the recent work. They talk about what worked well, what didn’t, and how they can improve. It’s not just about finding problems; it’s also about coming up with solutions and getting better over time. Pillar 3: Experience and Experimentation in Scrum The third pillar is all about trying things out and learning from those experiences. In Scrum, this happens during Sprint Planning and the actual sprints. The team plans what they’ll work on based on past experiences and feedback. Then, during the sprint, they experiment with their plans. They try things out, see what works, and adjust their approach. It’s a continuous cycle of learning and improving. Connections in Scrum: These three pillars work together like a team. Sensation gives the team real-time information. Reflection helps them think about what’s happening and make improvements. Experience and Experimentation let the team try things out and learn from their actions. It’s a cycle that keeps going, helping the team adapt and succeed. Scrum’s Impact: Scrum’s success comes from using these Three Pillars of Empiricism. It helps teams manage projects by being flexible and learning from each experience. The way Scrum works, with its regular check-ins and constant improvements, ensures that teams can handle changes and deliver good results consistently. Conclusion: The Three Pillars of Empiricism—Sensation, Reflection, and Experience/Experimentation—are not just philosophical ideas; they are the guiding principles of Scrum. By paying attention to what’s happening, thinking about how to get better, and continuously learning from experiences, Scrum teams create a way of working that adapts to the challenges of project management. Embracing these principles, Scrum not only helps teams deliver great products but also fosters a culture of working together, being transparent, and always finding ways to improve—a true reflection of the power of learning from experience in the world of Agile methodologies.
Easy Ways to Keep an Eye on Your Scrum Team’s Progress

In the world of software development, Scrum teams work together to get things done. To make sure your Scrum team is doing well, it’s important to measure and track their progress. In this blog, we’ll explore simple ways to do that without getting too complicated. Defining Success: Figuring Out What Matters Before we start, let’s think about what success means for your team. Look for signs like how much work gets done in a sprint or if the team is facing any challenges. These signs are called key performance indicators (KPIs), and they help you see if you’re on the right track. Burndown Charts: Watching Work Disappear Imagine a chart that shows how much work is left in a sprint. That’s a burndown chart. A good burndown chart goes down steadily, showing progress. If it goes all over the place, it might mean there are problems or changes happening. Sprint Burnup Charts: Keeping an Eye on Workload Sprint burnup charts help you see if the team is finishing what they planned for a sprint. It’s like checking if you’re on track with your to-do list. If everything is going smoothly, the chart looks balanced. If there are sudden increases, it could mean unexpected work or changes in plans. Velocity: Checking How Fast You’re Going Velocity is a fancy word that means how much work your team can do in a sprint. Keep an eye on it over time. If it stays about the same, your team is doing well. Big changes might mean something is going wrong or the team is adjusting to new things. Cycle Time: Counting the Days Cycle time is how long it takes to finish a task from start to finish. Short cycle times are good—it means things are moving quickly. If it takes a long time, there might be problems that need fixing. Escaped Defects: Checking for Mistakes Nobody likes mistakes. Escaped defects are like problems that sneak through and are found later. Try to have as few of these as possible by doing thorough testing and fixing issues before they become big problems. Team Satisfaction: Keeping Everyone Happy Beyond all the numbers, it’s important to make sure your team is happy. Ask them how they feel and if they’re facing any challenges. A happy team works better and produces better results. Adapt and Iterate: Changing Course When Needed Remember, it’s okay to change things if they’re not working. Keep checking if your measurements make sense, and if they don’t, find new ones. Being flexible and always trying to improve is the key to success. Conclusion: Sailing Smoothly Measuring your Scrum team’s progress is like navigating a ship. By using simple tools like burndown charts, velocity, and keeping the team happy, you can steer your ship in the right direction. The journey might have some ups and downs, but with a flexible and positive approach, your Scrum team can sail smoothly to success.

