Introduction
In a rapidly changing business landscape, organizations need to embrace agility to stay competitive. However, scaling agile practices beyond individual teams can pose significant challenges. This is where SAFe (Scaled Agile Framework) comes into play. SAFe Agile offers a comprehensive framework that enables enterprises to successfully implement and scale agile methodologies. In this blog post, we will explore the fundamentals of SAFe Agile, its core principles, and the key components that make it an invaluable asset for organizations embarking on large-scale agile transformations.
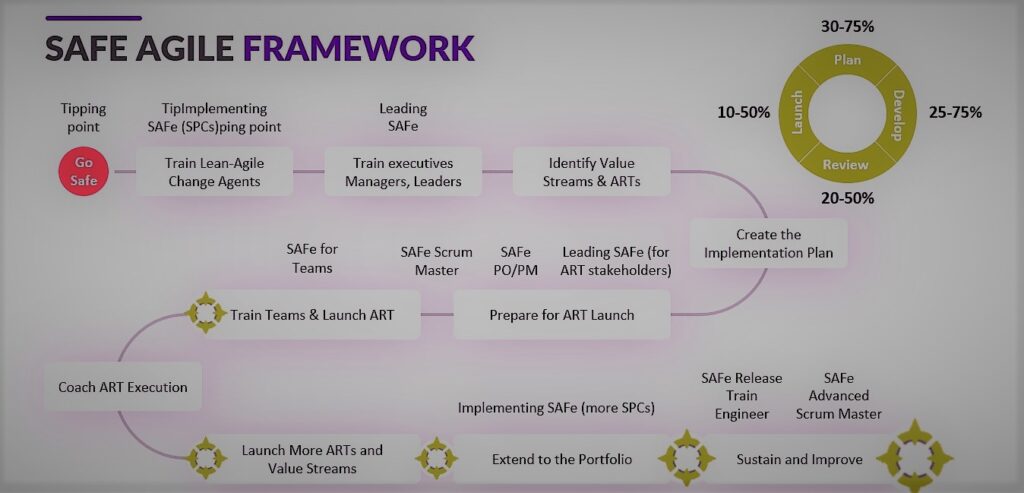
1. Understanding SAFe Agile
SAFe Agile is a robust framework designed to help organizations implement agile practices across the enterprise. It provides a structured approach that allows multiple teams to work cohesively while ensuring alignment, collaboration, and efficient delivery of value. SAFe Agile extends the principles of agility beyond individual teams, enabling organizations to maintain adaptability and customer-centricity at scale.
2. Core Principles of SAFe Agile
At the heart of SAFe Agile lie several core principles that drive its implementation:
a) Lean-Agile Mindset: SAFe Agile emphasizes a continuous improvement mindset, lean thinking, and delivering value to customers.
b) Systems Thinking: SAFe Agile promotes holistic thinking, recognizing the interconnectedness and dependencies among various components, teams, and stakeholders.
c) Alignment: Aligning all teams and stakeholders towards a common mission and vision, SAFe Agile fosters collaboration, breaks down silos, and ensures synchronized efforts.
d) Built-in Quality: SAFe Agile places a strong emphasis on maintaining high-quality standards throughout the entire development process, reducing defects and rework.
e) Transparency: SAFe Agile encourages openness and transparency, facilitating effective communication, visibility, and shared understanding across all levels of the organization.
f) Program Execution: SAFe Agile supports decentralized decision-making, fast feedback cycles, and iterative development through the implementation of Agile Release Trains (ARTs).
3. Key Components of SAFe Agile
SAFe Agile encompasses several key components that work synergistically to enable enterprise-scale agility:
a) Agile Release Train (ART): ART is the primary organizing construct in SAFe Agile, bringing together multiple teams aligned to a shared mission and working collaboratively to deliver value within fixed time increments called Program Increments (PIs).
b) Program Increment (PI): PI represents a timebox lasting 8-12 weeks during which ARTs plan, execute, and deliver valuable features and functionalities. PI Planning is a crucial event where teams align their efforts, address dependencies, and establish a synchronized roadmap.
c) Value Stream: SAFe Agile recognizes the importance of value streams, which encompass all the activities, processes, and stakeholders involved in delivering value to the customer. Mapping and optimizing the value stream ensure efficient value delivery.
d) Agile Teams: SAFe Agile promotes the formation of self-organizing, cross-functional teams that work together to deliver value incrementally. These teams follow agile methodologies such as Scrum or Kanban and synchronize their efforts within the ART.
e) Continuous Integration and Continuous Deployment (CI/CD): SAFe Agile encourages the adoption of DevOps practices, automated testing, and continuous integration to enable frequent and reliable integration, testing, and deployment of software.
4. Benefits of SAFe Agile
Implementing SAFe Agile brings numerous advantages to organizations:
a) Improved Collaboration and Alignment: SAFe Agile fosters collaboration, transparency, and shared objectives, resulting in improved alignment and coordination across teams and departments.
b) Increased Productivity and Time to Market: By scaling agile practices, SAFe Agile enables faster delivery of high-quality products and services, reducing time to market and enhancing productivity.
c) Enhanced Quality and Reduced Risk: SAFe Agile’s focus on built-in quality, iterative feedback loops, and continuous improvement leads to enhanced product quality, higher customer satisfaction, and reduced risk.
d) Scalability and Flexibility: SAFe Agile provides a structured framework that allows organizations to scale their agile practices while maintaining adaptability and flexibility.
e) Empowered and Engaged Teams: SAFe Agile empowers teams by providing clear roles and responsibilities, promoting autonomy, and fostering employee engagement and satisfaction.
Conclusion
SAFe Agile acts as a guiding light for organizations seeking to embrace agility at the enterprise level. By embracing SAFe Agile’s core principles and leveraging its key components, organizations can unlock the full potential of agile practices, driving collaboration, productivity, and success in a rapidly evolving business landscape.